Android-热修复

目前,热修复的原理主要有两种技术,一是不需要启动APP就能实现修复,在Native层实现的。一种时需要启动APP,在JAVA层实现的。
App启动到一半的时候,所有需要发生变更的类已经被加载过了, 在Android系统中是无法对一个已经加载的类进行卸载的。腾讯的Tinker的方案是让ClassLoader去加载新的类,如果不重启App,原有的类还在虚拟机中,就无法加载新的类。因此需要冷启动后,抢先加载修复补丁中的新类,从而达到热修复的目的。
- Native层:andfix sophix (即时修复 不重启APP), andfix 缺陷:
- 只能支持方法的替换。而对于补丁类里面存在方法增加和减少,以及成员字段的增加和减少的情况,都是不适用的。一旦补丁类中出现了方法的增加和减少,就会导致这个类以及整个Dex的方法数的变化。方法数的变化伴随着方法索引的变化,这样在访问方法时就无法正常地索引到正确的方法了。
- JAVA层:Tinker robust等(需要启动APP)
1. 热修复方案
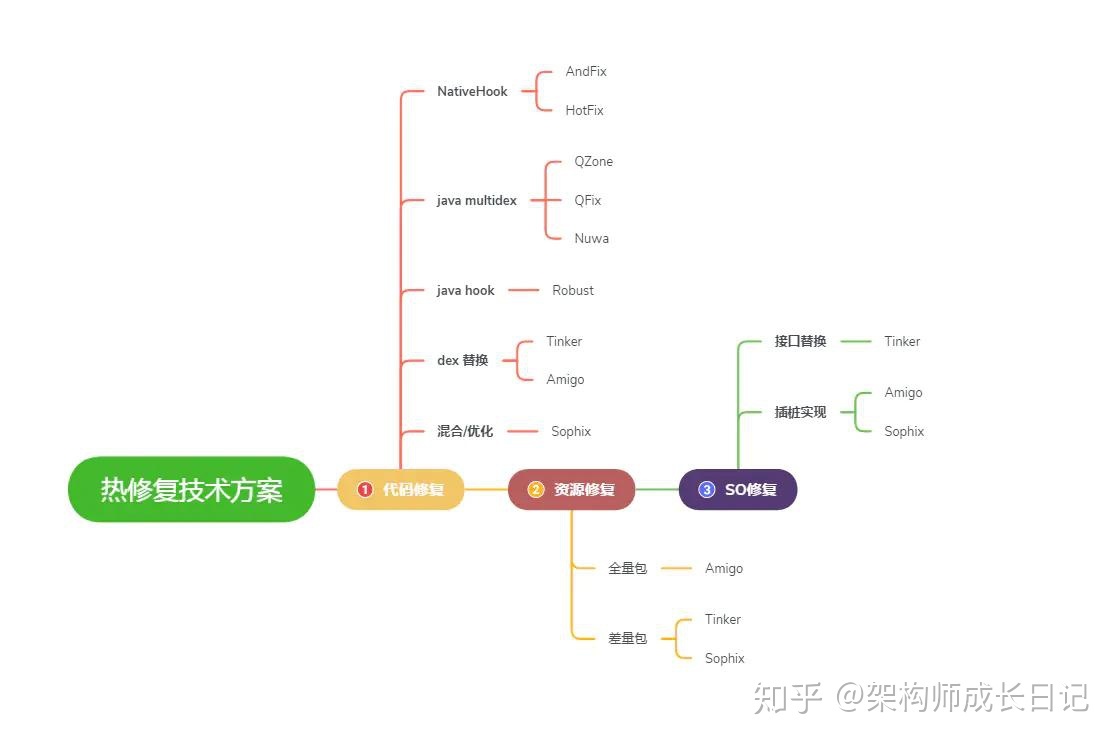
| 方案对比 | Sophix | Tinker | nuwa | AndFix | Robust | Amigo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 类替换 | yes | yes | yes | no | no | yes |
| So替换 | yes | yes | no | no | no | yes |
| 资源替换 | yes | yes | yes | no | no | yes |
| 全平台支持 | yes | yes | yes | no | yes | yes |
| 即时生效 | 同时支持 | no | no | yes | yes | no |
| 性能损耗 | 较少 | 较小 | 较大 | 较小 | 较小 | 较小 |
| 补丁包大小 | 小 | 较小 | 较大 | 一般 | 一般 | 较大 |
| 开发透明 | yes | yes | yes | no | no | yes |
| 复杂度 | 傻瓜式接入 | 复杂 | 较低 | 复杂 | 复杂 | 较低 |
| Rom体积 | 较小 | Dalvik较大 | 较小 | 较小 | 较小 | 大 |
| 成功率 | 高 | 较高 | 较高 | 一般 | 最高 | 较高 |
| 热度 | 高 | 高 | 低 | 低 | 高 | 低 |
| 开源 | no | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| 收费 | 收费(设有免费阈值) | 收费(基础版免费,但有限制) | 免费 | 免费 | 免费 | 免费 |
| 监控 | 提供分发控制及监控 | 提供分发控制及监控 | no | no | no |
2. Native 方式
1. AndFix 代码阅读
- 通过工具生成带@MethodReplace的dex.classes差分包。这个注解,是标示着类出现变化的地方
- 通过PatchManager 加载差分包
- 通过AndFixManager修复两个dex之间差异的类,用差分包代替掉原包中的差异。
每一个
Java方法在Art虚拟机中都对应一个 ArtMethod,ArtMethod 记录了该方法的所有信息,包括所属类、访问权限、代码执行地址等。通过env->FromReflectedMethod,可以由Method对象得到这个方法对应的ArtMethod的真正起始地址,然后强转为 ArtMethod 指针,通过指针的操作对其成员属性进行修改替换。
解析jar
private void init() throws IOException {
JarFile jarFile = null;
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
jarFile = new JarFile(mFile);
JarEntry entry = jarFile.getJarEntry(ENTRY_NAME); //"META-INF/PATCH.MF"
inputStream = jarFile.getInputStream(entry);
Manifest manifest = new Manifest(inputStream);
Attributes main = manifest.getMainAttributes();
mName = main.getValue(PATCH_NAME); //"Patch-Name"
mTime = new Date(main.getValue(CREATED_TIME));
mClassesMap = new HashMap<String, List<String>>();
Attributes.Name attrName;
String name;
List<String> strings;
for (Iterator<?> it = main.keySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
attrName = (Attributes.Name) it.next();
name = attrName.toString();
if (name.endsWith(CLASSES)) { //"-Classes"
strings = Arrays.asList(main.getValue(attrName).split(","));
if (name.equalsIgnoreCase(PATCH_CLASSES)) { //"Patch-Classes"
mClassesMap.put(mName, strings);
} else {
mClassesMap.put(
name.trim().substring(0, name.length() - 8),// remove
// "-Classes"
strings);
}
}
}
} finally {
if (jarFile != null) {
jarFile.close();
}
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close();
}
}
}
/**
* load patch,call when plugin be loaded. used for plugin architecture.</br>
*
* need name and classloader of the plugin
*
* @param patchName
* patch name
* @param classLoader
* classloader
*/
public void loadPatch(String patchName, ClassLoader classLoader) {
mLoaders.put(patchName, classLoader);
Set<String> patchNames;
List<String> classes;
for (Patch patch : mPatchs) {
patchNames = patch.getPatchNames();
if (patchNames.contains(patchName)) {
classes = patch.getClasses(patchName);
mAndFixManager.fix(patch.getFile(), classLoader, classes);
}
}
}
private void loadPatch(Patch patch) {
Set<String> patchNames = patch.getPatchNames();
ClassLoader cl;
List<String> classes;
for (String patchName : patchNames) {
if (mLoaders.containsKey("*")) {
cl = mContext.getClassLoader();
} else {
cl = mLoaders.get(patchName);
}
if (cl != null) {
classes = patch.getClasses(patchName);
mAndFixManager.fix(patch.getFile(), cl, classes);
}
}
}
解析DexFile
/**
* fix
*
* @param file
* patch file
* @param classLoader
* classloader of class that will be fixed
* @param classes
* classes will be fixed
*/
public synchronized void fix(File file, ClassLoader classLoader,
List<String> classes) {
try {
final DexFile dexFile = DexFile.loadDex(file.getAbsolutePath(),
optfile.getAbsolutePath(), Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
//todo? 这里没有太理解含义
ClassLoader patchClassLoader = new ClassLoader(classLoader) {
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String className)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> clazz = dexFile.loadClass(className, this);
if (clazz == null
&& className.startsWith("com.alipay.euler.andfix")) {
return Class.forName(className);// annotation’s class
// not found
}
if (clazz == null) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(className);
}
return clazz;
}
};
Enumeration<String> entrys = dexFile.entries();
Class<?> clazz = null;
while (entrys.hasMoreElements()) {
String entry = entrys.nextElement();
if (classes != null && !classes.contains(entry)) {
continue;// skip, not need fix
}
clazz = dexFile.loadClass(entry, patchClassLoader);
if (clazz != null) {
fixClass(clazz, classLoader);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "pacth", e);
}
}
注解找到要替换的方法
private void fixClass(Class<?> clazz, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
MethodReplace methodReplace;
String clz;
String meth;
for (Method method : methods) {
methodReplace = method.getAnnotation(MethodReplace.class);
if (methodReplace == null)
continue;
clz = methodReplace.clazz();
meth = methodReplace.method();
if (!isEmpty(clz) && !isEmpty(meth)) {
replaceMethod(classLoader, clz, meth, method);
}
}
}
调用jni函数实现方法替换
/**
* replace method
*
* @param classLoader classloader
* @param clz class
* @param meth name of target method
* @param method source method
*/
private void replaceMethod(ClassLoader classLoader, String clz,
String meth, Method method) {
try {
String key = clz + "@" + classLoader.toString();
Class<?> clazz = mFixedClass.get(key);
//当前的class发现又在差分包中,但是没有在缓存中,说明还有没有初始化这个class里面的属性,需要一次initTargetClass。
if (clazz == null) {// class not load
Class<?> clzz = classLoader.loadClass(clz);
// initialize target class
clazz = AndFix.initTargetClass(clzz);
}
if (clazz != null) {// initialize class OK
mFixedClass.put(key, clazz);
Method src = clazz.getDeclaredMethod(meth,
method.getParameterTypes());
AndFix.addReplaceMethod(src, method);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "replaceMethod", e);
}
}
AndFix 方法
private static native boolean setup(boolean isArt, int apilevel);
private static native void replaceMethod(Method dest, Method src);
private static native void setFieldFlag(Field field);
Native 方法
static jboolean setup(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jboolean isart,
jint apilevel) {
isArt = isart;
LOGD("vm is: %s , apilevel is: %i", (isArt ? "art" : "dalvik"),
(int )apilevel);
if (isArt) {
return art_setup(env, (int) apilevel);
} else {
return dalvik_setup(env, (int) apilevel);
}
}
static void replaceMethod(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jobject src,
jobject dest) {
if (isArt) {
art_replaceMethod(env, src, dest);
} else {
dalvik_replaceMethod(env, src, dest);
}
}
static void setFieldFlag(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jobject field) {
if (isArt) {
art_setFieldFlag(env, field);
} else {
dalvik_setFieldFlag(env, field);
}
}
void replace_4_4(JNIEnv* env, jobject src, jobject dest);
void setFieldFlag_4_4(JNIEnv* env, jobject field);
void replace_5_0(JNIEnv* env, jobject src, jobject dest);
void setFieldFlag_5_0(JNIEnv* env, jobject field);
void replace_5_1(JNIEnv* env, jobject src, jobject dest);
void setFieldFlag_5_1(JNIEnv* env, jobject field);
void replace_6_0(JNIEnv* env, jobject src, jobject dest);
void setFieldFlag_6_0(JNIEnv* env, jobject field);
void replace_7_0(JNIEnv* env, jobject src, jobject dest);
void setFieldFlag_7_0(JNIEnv* env, jobject field);
setFieldFlag 函数
void setFieldFlag_7_0(JNIEnv* env, jobject field) {
art:🪞:ArtField* artField =
(art:🪞:ArtField*) env->FromReflectedField(field);
//本质上是要把当前的属性全部转化为public的方法
artField->access_flags_ = artField->access_flags_ & (~0x0002) | 0x0001;
LOGD("setFieldFlag_7_0: %d ", artField->access_flags_);
}
1.ACC_PUBLIC 0x0001
2.ACC_PRIVATE 0x0002
3.ACC_PROTECTED 0x0004
4.ACC_STATIC 0x0008
5.ACC_FINAL 0x0010
6.ACC_VOLATILE 0x0040
6.ACC_TRANSIENT 0x0080
6.ACC_SYNTHENTIC 0x1000
6.ACC_ENUM 0x4000
replace
void replace_7_0(JNIEnv* env, jobject src, jobject dest) {
art:🪞:ArtMethod* smeth =
(art:🪞:ArtMethod*) env->FromReflectedMethod(src);
art:🪞:ArtMethod* dmeth =
(art:🪞:ArtMethod*) env->FromReflectedMethod(dest);
// reinterpret_cast<art:🪞:Class*>(smeth->declaring_class_)->class_loader_ =
// reinterpret_cast<art:🪞:Class*>(dmeth->declaring_class_)->class_loader_; //for plugin classloader
reinterpret_cast<art:🪞:Class*>(dmeth->declaring_class_)->clinit_thread_id_ =
reinterpret_cast<art:🪞:Class*>(smeth->declaring_class_)->clinit_thread_id_;
reinterpret_cast<art:🪞:Class*>(dmeth->declaring_class_)->status_ =
reinterpret_cast<art:🪞:Class*>(smeth->declaring_class_)->status_ -1;
//for reflection invoke
reinterpret_cast<art:🪞:Class*>(dmeth->declaring_class_)->super_class_ = 0;
smeth->declaring_class_ = dmeth->declaring_class_;
smeth->access_flags_ = dmeth->access_flags_ | 0x0001;
smeth->dex_code_item_offset_ = dmeth->dex_code_item_offset_;
smeth->dex_method_index_ = dmeth->dex_method_index_;
smeth->method_index_ = dmeth->method_index_;
smeth->hotness_count_ = dmeth->hotness_count_;
smeth->ptr_sized_fields_.dex_cache_resolved_methods_ =
dmeth->ptr_sized_fields_.dex_cache_resolved_methods_;
smeth->ptr_sized_fields_.dex_cache_resolved_types_ =
dmeth->ptr_sized_fields_.dex_cache_resolved_types_;
smeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_jni_ =
dmeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_jni_;
smeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_ =
dmeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_;
LOGD("replace_7_0: %d , %d",
smeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_,
dmeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_);
}

ArtField & ArtMethod
class ArtField {
public:
uint32_t declaring_class_;
uint32_t access_flags_;
uint32_t field_dex_idx_;
uint32_t offset_;
};
class ArtMethod {
public:
// Field order required by test "ValidateFieldOrderOfJavaCppUnionClasses".
// The class we are a part of.
uint32_t declaring_class_;
// Access flags; low 16 bits are defined by spec.
uint32_t access_flags_;
/* Dex file fields. The defining dex file is available via declaring_class_->dex_cache_ */
// Offset to the CodeItem.
uint32_t dex_code_item_offset_;
// Index into method_ids of the dex file associated with this method.
uint32_t dex_method_index_;
/* End of dex file fields. */
// Entry within a dispatch table for this method. For static/direct methods the index is into
// the declaringClass.directMethods, for virtual methods the vtable and for interface methods the
// ifTable.
uint16_t method_index_;
// The hotness we measure for this method. Incremented by the interpreter. Not atomic, as we allow
// missing increments: if the method is hot, we will see it eventually.
uint16_t hotness_count_;
// Fake padding field gets inserted here.
// Must be the last fields in the method.
// PACKED(4) is necessary for the correctness of
// RoundUp(OFFSETOF_MEMBER(ArtMethod, ptr_sized_fields_), pointer_size).
struct PtrSizedFields {
// Short cuts to declaring_class_->dex_cache_ member for fast compiled code access.
ArtMethod** dex_cache_resolved_methods_;
// Short cuts to declaring_class_->dex_cache_ member for fast compiled code access.
void* dex_cache_resolved_types_;
// Pointer to JNI function registered to this method, or a function to resolve the JNI function,
// or the profiling data for non-native methods, or an ImtConflictTable.
void* entry_point_from_jni_;
// Method dispatch from quick compiled code invokes this pointer which may cause bridging into
// the interpreter.
void* entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_;
} ptr_sized_fields_;
};
2. MethodHook
public class MethodHook {
public static void m1(){}
public static void m2(){}
private Map<Method, Long> methodBackup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public void hook(Method src, Method dest) {
if (src == null || dest == null) {
return;
}
if (!methodBackup.containsKey(src)) {
methodBackup.put(src, hook_native(src, dest));
}
}
public void restore(Method src) {
if (src == null) {
return;
}
Long srcMethodPtr = methodBackup.get(src);
if (srcMethodPtr != null) {
methodBackup.remove(restore_native(src, srcMethodPtr));
}
}
private static native long hook_native(Method src, Method dest);
private static native Method restore_native(Method src, long methodPtr);
static {
System.loadLibrary("method-hook-lib");
}
}
native 实现
static struct {
jmethodID m1;
jmethodID m2;
size_t methodSize;
} methodHookClassInfo;
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM* vm, void* reserved) {
JNIEnv *env = nullptr;
if (vm->GetEnv((void **) &env, JNI_VERSION_1_4) != JNI_OK) {
return JNI_FALSE;
}
jclass classEvaluateUtil = env->FindClass(kClassMethodHookChar);
if(env -> RegisterNatives(classEvaluateUtil, gMethods, sizeof(gMethods)/ sizeof(gMethods[0])) < 0) {
return JNI_FALSE;
}
//ArtMethod数组仍是以线性结构排列
methodHookClassInfo.m1 = env -> GetStaticMethodID(classEvaluateUtil, "m1", "()V");
methodHookClassInfo.m2 = env -> GetStaticMethodID(classEvaluateUtil, "m2", "()V");
methodHookClassInfo.methodSize = reinterpret_cast<size_t>(methodHookClassInfo.m2) - reinterpret_cast<size_t>(methodHookClassInfo.m1);
return JNI_VERSION_1_4;
}
static long methodHook(JNIEnv* env, jclass type, jobject srcMethodObj, jobject destMethodObj) {
void* srcMethod = reinterpret_cast<void*>(env -> FromReflectedMethod(srcMethodObj));
void* destMethod = reinterpret_cast<void*>(env -> FromReflectedMethod(destMethodObj));
int* backupMethod = new int[methodHookClassInfo.methodSize];
memcpy(backupMethod, srcMethod, methodHookClassInfo.methodSize);
memcpy(srcMethod, destMethod, methodHookClassInfo.methodSize);
return reinterpret_cast(backupMethod);
}
static jobject methodRestore(JNIEnv* env, jclass type, jobject srcMethod, jlong methodPtr) {
int* backupMethod = reinterpret_cast<int*>(methodPtr);
void* artMethodSrc = reinterpret_cast<void*>(env -> FromReflectedMethod(srcMethod));
memcpy(artMethodSrc, backupMethod, methodHookClassInfo.methodSize);
delete []backupMethod;
return srcMethod;
}

3. JavaHook原理
1、打基础包时插桩,在每个方法前插入一段类型为 ChangeQuickRedirect 静态变量的逻辑,插入过程对业务开发是完全透明
2、加载补丁时,从补丁包中读取要替换的类及具体替换的方法实现,新建ClassLoader加载补丁dex。当changeQuickRedirect不为null时,可能会执行到accessDispatch从而替换掉之前老的逻辑,达到fix的目的
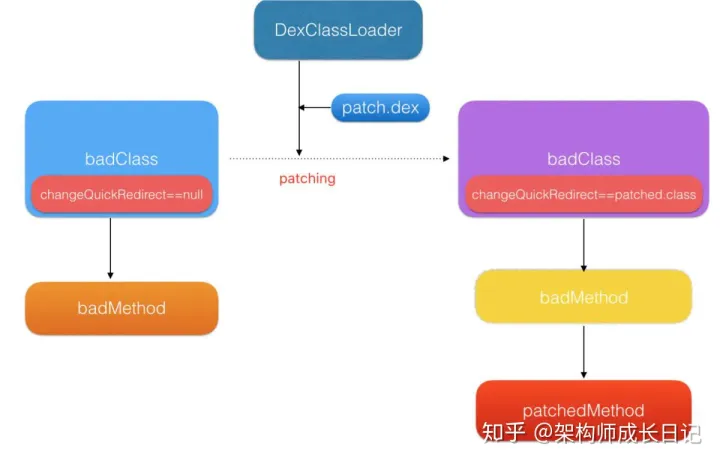
public static ChangeQuickRedirect u;
protected void onCreate(Bundle bundle) {
//为每个方法自动插入修复逻辑代码,如果ChangeQuickRedirect为空则不执行
if (u != null) {
if (PatchProxy.isSupport(new Object[]{bundle}, this, u, false, 78)) {
PatchProxy.accessDispatchVoid(new Object[]{bundle}, this, u, false, 78);
return;
}
}
super.onCreate(bundle);
...
}
public class PatchExecutor extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
...
applyPatchList(patches);
...
}
/**
* 应用补丁列表
*/
protected void applyPatchList(List<Patch> patches) {
...
for (Patch p : patches) {
...
currentPatchResult = patch(context, p);
...
}
}
/**
* 核心修复源码
*/
protected boolean patch(Context context, Patch patch) {
...
//新建ClassLoader
DexClassLoader classLoader = new DexClassLoader(patch.getTempPath(), context.getCacheDir().getAbsolutePath(),
null, PatchExecutor.class.getClassLoader());
patch.delete(patch.getTempPath());
...
try {
patchsInfoClass = classLoader.loadClass(patch.getPatchesInfoImplClassFullName());
patchesInfo = (PatchesInfo) patchsInfoClass.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
...
//通过遍历其中的类信息进而反射修改其中 ChangeQuickRedirect 对象的值
for (PatchedClassInfo patchedClassInfo : patchedClasses) {
...
try {
oldClass = classLoader.loadClass(patchedClassName.trim());
Field[] fields = oldClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (TextUtils.equals(field.getType().getCanonicalName(), ChangeQuickRedirect.class.getCanonicalName()) && TextUtils.equals(field.getDeclaringClass().getCanonicalName(), oldClass.getCanonicalName())) {
changeQuickRedirectField = field;
break;
}
}
...
try {
patchClass = classLoader.loadClass(patchClassName);
Object patchObject = patchClass.newInstance();
changeQuickRedirectField.setAccessible(true);
changeQuickRedirectField.set(null, patchObject);
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
}
return true;
}
}
4. java mulitdex 原理
Android内部使用的是
BaseDexClassLoader、PathClassLoader、DexClassLoader三个类加载器实现从DEX文件中读取类数据,其中PathClassLoader和DexClassLoader都是继承自BaseDexClassLoader实现。dex文件转换成dexFile对象,存入Element[]数组,findclass顺序遍历Element数组获取DexFile,然后执行DexFile的findclass。
Hook了ClassLoader.pathList.dexElements[],将补丁的dex插入到数组的最前端。因为ClassLoader的findClass是通过遍历dexElements[]中的dex来寻找类的。所以会优先查找到修复的类。从而达到修复的效果。
// 加载名字为name的class对象
public Class findClass(String name, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
// 遍历从dexPath查询到的dex和资源Element
for (Element element : dexElements) {
DexFile dex = element.dexFile;
// 如果当前的Element是dex文件元素
if (dex != null) {
// 使用DexFile.loadClassBinaryName加载类
Class clazz = dex.loadClassBinaryName(name, definingContext, suppressed);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
}
}
}
if (dexElementsSuppressedExceptions != null) {
suppressed.addAll(Arrays.asList(dexElementsSuppressedExceptions));
}
return null;
}
public static void injectDexAtFirst(String dexPath, String defaultDexOptPath) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
//新建一个ClassLoader加载补丁Dex
DexClassLoader dexClassLoader = new DexClassLoader(dexPath, defaultDexOptPath, dexPath, getPathClassLoader());
//反射获取旧DexElements数组
Object baseDexElements = getDexElements(getPathList(getPathClassLoader()));
//反射获取补丁DexElements数组
Object newDexElements = getDexElements(getPathList(dexClassLoader));
//合并,将新数组的Element插入到最前面
Object allDexElements = combineArray(newDexElements, baseDexElements);
Object pathList = getPathList(getPathClassLoader());
//更新旧ClassLoader中的Element数组
ReflectionUtils.setField(pathList, pathList.getClass(), "dexElements", allDexElements);
}
private static PathClassLoader getPathClassLoader() {
PathClassLoader pathClassLoader = (PathClassLoader) DexUtils.class.getClassLoader();
return pathClassLoader;
}
private static Object getDexElements(Object paramObject)
throws IllegalArgumentException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
return ReflectionUtils.getField(paramObject, paramObject.getClass(), "dexElements");
}
private static Object getPathList(Object baseDexClassLoader)
throws IllegalArgumentException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
return ReflectionUtils.getField(baseDexClassLoader, Class.forName("dalvik.system.BaseDexClassLoader"), "pathList");
}
private static Object combineArray(Object firstArray, Object secondArray) {
Class<?> localClass = firstArray.getClass().getComponentType();
int firstArrayLength = Array.getLength(firstArray);
int allLength = firstArrayLength + Array.getLength(secondArray);
Object result = Array.newInstance(localClass, allLength);
for (int k = 0; k < allLength; ++k) {
if (k < firstArrayLength) {
Array.set(result, k, Array.get(firstArray, k));
} else {
Array.set(result, k, Array.get(secondArray, k - firstArrayLength));
}
}
return result;
}
5. dex替换
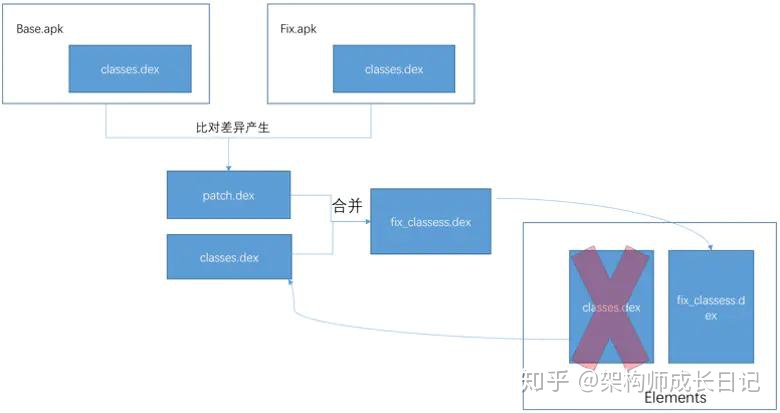
dex差量包,整体替换dex的方案。差量的方式给出patch.dex,然后将patch.dex与应用的classes.dex合并成一个完整的dex,完整dex加载得到dexFile对象作为参数构建一个Element对象然后整体替换掉旧的dex-Elements数组。
Tinker自研了
DexDiff/DexMerge算法。Tinker还支持资源和So包的更新,So补丁包使用BsDiff来生成,资源补丁包直接使用文件md5对比来生成,针对资源比较大的(默认大于100KB属于大文件)会使用BsDiff来对文件生成差量补丁
6. so修复原理
1. 接口替换
sdk提供接口替换System默认加载so库的接口, SOPatchManger.loadLibrary接口加载so库的时候优先尝试去加载sdk指定目录下补丁的so。若不存在,则再去加载安装apk目录下的so库
SOPatchManger.loadLibrary(String libName)
//替换
System.loadLibrary(String libName)
2. 反射注入
采取类似类修复反射注入方式,只要把补丁so库的路径插入到nativeLibraryDirectories数组的最前面,就能够达到加载so库的时候是补丁so库而不是原来so库的目录,从而达到修复。
public String findLibrary(String libraryName) {
String fileName = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
for (NativeLibraryElement element : nativeLibraryPathElements) {
String path = element.findNativeLibrary(fileName);
if (path != null) {
return path;
}
}
return null;
}
7. 资源修复原理
1、构建一个新的AssetManager,并通过反射调用addAssertPath,把这个完整的新资源包加入到AssetManager中。这样就得到一个含有所有新资源的AssetManager
2、找到所有之前引用到原有AssetManager的地方,通过反射,把引用处替换为AssetManager
public static void monkeyPatchExistingResources(Context context,
String externalResourceFile, Collection activities) {
if (externalResourceFile == null) {
return;
}
try {
//反射一个新的 AssetManager
AssetManager newAssetManager = (AssetManager) AssetManager.class
.getConstructor(new Class[0]).newInstance(new Object[0]);
//反射 addAssetPath 添加新的资源包
Method mAddAssetPath = AssetManager.class.getDeclaredMethod("addAssetPath", new Class[]{String.class});
mAddAssetPath.setAccessible(true);
if (((Integer) mAddAssetPath.invoke(newAssetManager,
new Object[]{externalResourceFile})).intValue() == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Could not create new AssetManager");
}
Method mEnsureStringBlocks = AssetManager.class.getDeclaredMethod("ensureStringBlocks", new Class[0]);
mEnsureStringBlocks.setAccessible(true);
mEnsureStringBlocks.invoke(newAssetManager, new Object[0]);
//反射得到Activity中AssetManager的引用处,全部换成刚新构建的AssetManager对象
if (activities != null) {
for (Activity activity : activities) {
Resources resources = activity.getResources();
try {
Field mAssets = Resources.class.getDeclaredField("mAssets");
mAssets.setAccessible(true);
mAssets.set(resources, newAssetManager);
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
Field mResourcesImpl = Resources.class.getDeclaredField("mResourcesImpl");
mResourcesImpl.setAccessible(true);
Object resourceImpl = mResourcesImpl.get(resources);
Field implAssets = resourceImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("mAssets");
implAssets.setAccessible(true);
implAssets.set(resourceImpl, newAssetManager);
}
Resources.Theme theme = activity.getTheme();
try {
try {
Field ma = Resources.Theme.class.getDeclaredField("mAssets");
ma.setAccessible(true);
ma.set(theme, newAssetManager);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException ignore) {
Field themeField = Resources.Theme.class.getDeclaredField("mThemeImpl");
themeField.setAccessible(true);
Object impl = themeField.get(theme);
Field ma = impl.getClass().getDeclaredField("mAssets");
ma.setAccessible(true);
ma.set(impl, newAssetManager);
}
Field mt = ContextThemeWrapper.class.getDeclaredField("mTheme");
mt.setAccessible(true);
mt.set(activity, null);
Method mtm = ContextThemeWrapper.class.getDeclaredMethod("initializeTheme", new Class[0]);
mtm.setAccessible(true);
mtm.invoke(activity, new Object[0]);
Method mCreateTheme = AssetManager.class.getDeclaredMethod("createTheme", new Class[0]);
mCreateTheme.setAccessible(true);
Object internalTheme = mCreateTheme.invoke(newAssetManager, new Object[0]);
Field mTheme = Resources.Theme.class.getDeclaredField("mTheme");
mTheme.setAccessible(true);
mTheme.set(theme, internalTheme);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Log.e("InstantRun",
"Failed to update existing theme for activity "
+ activity, e);
}
pruneResourceCaches(resources);
}
}
Collection references;
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 19) {
Class resourcesManagerClass = Class.forName("android.app.ResourcesManager");
Method mGetInstance = resourcesManagerClass.getDeclaredMethod("getInstance", new Class[0]);
mGetInstance.setAccessible(true);
Object resourcesManager = mGetInstance.invoke(null, new Object[0]);
try {
Field fMActiveResources = resourcesManagerClass.getDeclaredField("mActiveResources");
fMActiveResources.setAccessible(true);
ArrayMap arrayMap = (ArrayMap) fMActiveResources.get(resourcesManager);
references = arrayMap.values();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException ignore) {
Field mResourceReferences = resourcesManagerClass.getDeclaredField("mResourceReferences");
mResourceReferences.setAccessible(true);
references = (Collection) mResourceReferences.get(resourcesManager);
}
} else {
Class activityThread = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread");
Field fMActiveResources = activityThread.getDeclaredField("mActiveResources");
fMActiveResources.setAccessible(true);
Object thread = getActivityThread(context, activityThread);
HashMap map = (HashMap) fMActiveResources.get(thread);
references = map.values();
}
for (WeakReference wr : references) {
Resources resources = (Resources) wr.get();
if (resources != null) {
try {
Field mAssets = Resources.class.getDeclaredField("mAssets");
mAssets.setAccessible(true);
mAssets.set(resources, newAssetManager);
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
Field mResourcesImpl = Resources.class.getDeclaredField("mResourcesImpl");
mResourcesImpl.setAccessible(true);
Object resourceImpl = mResourcesImpl.get(resources);
Field implAssets = resourceImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("mAssets");
implAssets.setAccessible(true);
implAssets.set(resourceImpl, newAssetManager);
}
resources.updateConfiguration(resources.getConfiguration(), resources.getDisplayMetrics());
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
}
Resource
- AndFix: https://github.com/alibaba/AndFix
- Android虚拟机Art和Dalvik的区别:https://blog.csdn.net/johnWcheung/article/details/102657024
- Jar 文件读取: https://blog.csdn.net/ywg_1994/article/details/104440114
- MethodHook方法:https://juejin.cn/post/6844903486656626702, https://github.com/pqpo/MethodHook
- 热修复后,同包中权限问题和反射调用问题:https://developer.aliyun.com/article/74598#slide-4
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/336081084
- 热修复方案对比: https://juejin.cn/post/6844903527903395848#heading-31
- andfix, tinker 实践:https://www.jianshu.com/p/a76b72daf1bc#h5o-13