blobstore&blobfs

目录
Blobstore是位于SPDK bdev之上的Blob管理层,用于与用户态文件系统Blobstore Filesystem (BlobFS)集成,从而代替传统的文件系统,支持更上层的服务,如数据库MySQL、K-V存储引擎Rocksdb以及分布式存储系统Ceph、Cassandra等。**以Rocksdb为例,通过BlobFS作为Rocksdb的存储后端的优势在于,I/O经由BlobFS与Blobstore下发到bdev,随后由SPDK用户态driver写入磁盘。整个I/O流从发起到落盘均在用户态操作,完全bypass内核。**此外,可以充分利用SPDK所提供的异步、无锁化、Zero Copy、轮询等机制,大幅度减少额外的系统开销。
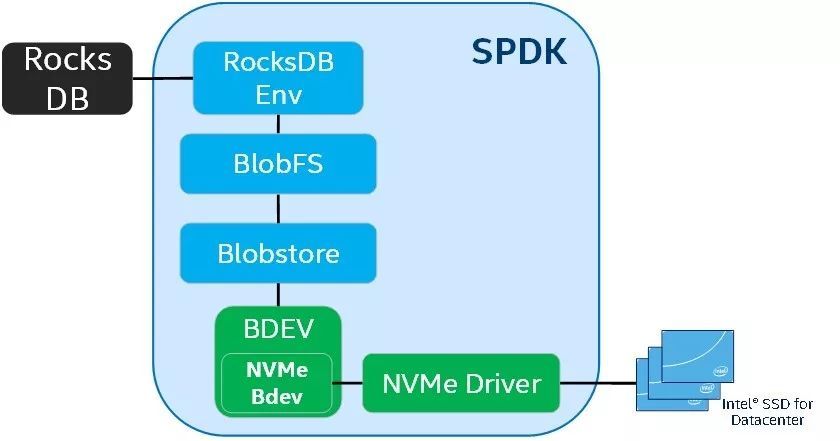
BlobStore 架构
BlobStore在BlueStore的工作上简化了许多功能,同时也增加了分层缓存功能,所以大致上和BlueStore的架构很类似。
BlockDevice:物理块设备,直接操作裸设备,支持KernelDevice(内核态异步IO)、NVMEDevice(SPDK用户态IO);同时提供分层缓存的功能。RocksDB:存储WAL、对象元数据、磁盘分配器元数据。Allocator:磁盘分配器,使用bitmap磁盘分配器,负责高效的分配磁盘空间。SPDK:使用spdk提供的blobfs、blobstore来支持rocksdb的存储,也可使用BlueStore的。FreeListManager:使用bitmap方式来管理空闲空间列表。Cache:主要用来缓存元数据,可缓存部分数据,数据主要缓存在BlockDevice提供的缓存里。- BlueStore源码分析之BlockDevice
- BlueStore源码分析之BitMap分配器
- BlueStore源码分析之FreelistManager
- BlueStore源码分析之Cache
- BlueStore源码分析之对象IO
BlobFS & Blobstore 关系
- Blobstore的设计可以在一个块设备上,进行异步、未压缩、并行读写,这个块设备会被分为很多组块,这些块称为“blobs”。
- BlobFS在管理文件时,主要
依赖于Blobstore对blob的分配与管理。Blob类似于文件的概念,而又不完全等同于文件,其并不支持所有文件的POSIX接口。 - BlobFS与Blobstore的关系可以理解为
Blobstore实现了对Blob的管理,包括Blob的分配、删除、读取、写入、元数据的管理等,而BlobFS是在Blobstore的基础上进行封装的一个轻量级文件系统,用于提供部分对于文件操作的接口,并将对文件的操作转换为对Blob的操作,BlobFS中的文件与Blobstore中的Blob一一对应。 - 在Blobstore下层,与SPDK bdev层对接。SPDK bdev层类似于内核中的
通用块设备层,是对底层不同类型设备的统一抽象管理,例如NVMe bdev、Malloc bdev、AIO bdev等。
Blobstore中结构的划分
- 在blobstore中,将SSD中的块划分为多个抽象层,主要由Logical Block、Page、Cluster、Blob组成
- Logical Block:
与块设备中所提供的逻辑块相对应,通常为512B或4KiB。实际硬盘存储的基本单位。 - Page:由多个连续的Logical Block构成,通常一个page的大小为4KiB,因此一个Page由八个或一个Logical Block构成,取决于Logical Block的大小。在Blobstore中,
Page是连续的,即从SSD的LBA 0开始,多个或一个块构成Page 0,接下来是Page 1,依次类推。 - Cluster:
由多个连续的Page构成,通常一个Cluster的大小默认为1MiB,因此一个Cluster由256个Page构成。Cluster与Page一样,是连续的,即从SSD的LBA 0开始的位置依次为Cluster 0到Cluster N。 - Blob:Blobstore中主要的操作对象为Blob,与BlobFS中的文件相对应,提供read、write、create、delete等操作。
一个Blob由多个Cluster构成,但构成Blob中的Cluster并不一定是连续的。
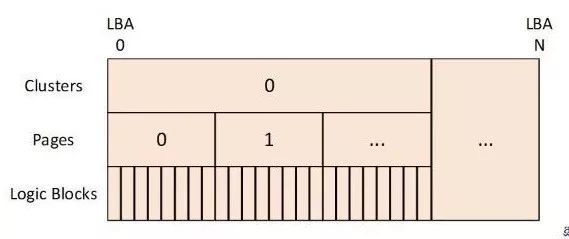
Blobstore 块管理与分配
- 在Blobstore中,会将cluster 0作为一个特殊的cluster。该cluster用于存放
Blobtore的所有信息以及元数据,对每个blob数据块的查找、分配都是依赖cluster 0中所记录的元数据所进行的。 - Cluster 0中的第一个page作为super block,Blobstore初始化后的一些基本信息都存放在super block中,例如cluster的大小、已使用page的起始位置、已使用page的个数、已使用cluster的起始位置、已使用cluster的个数、Blobstore的大小等信息。
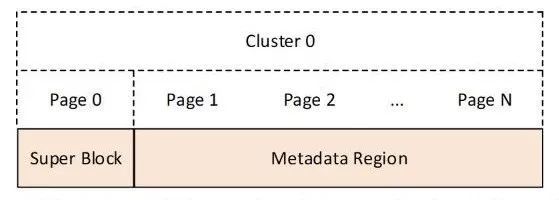

- Metadata Page Allocation:用于记录
所有元数据页的分配情况。在分配或释放元数据页后,将会对metadata page allocation中的数据做相应的修改。 - Cluster Allocation:用于记录
所有cluster的分配情况。在分配新的cluster或释放cluster后会对cluster allocation中的数据做相应的修改。 - Blob Id Allocation:用于记录
blob id的分配情况。对于blobstore中的所有blob,都是通过唯一的标识符blob id将其对应起来。在元数据域中,将会在blob allocation中记录所有的blob id分配情况。 - Metadata Pages Region:元数据页区域中
存放着每个blob的元数据页。每个blob中所分配的cluster都会记录在该blob的元数据页中,在读写blob时,首先会通过blob id定位到该blob的元数据页,其次根据元数据页中所记录的信息,检索到对应的cluster。对于每个blob的元数据页,并不是连续的。 - 在创建blob时,首先会为其分配blob id以及metadata page,其次更新metadata region。当对blob进行写入时,首先会为其分配cluster,其次更新该blob的metadata page,最后将数据写入,并持久化到磁盘中。
Blob 使用说明
- 原子性:对于所有blobstore 的操作原子性保证,都由底层来保证操作一个page的原子性。
- 数据写入:写入的数据通过以page为单位。每个page写入之后就会保存。举例:如果一个page更新数据时断电了,那么这个page的数据将不会写入新数据。也就是他不会更新。
- 异步回调:blobstore 是回调驱动的,如果blolbstore中的某个API不能够继续进行,他不会阻塞住其他的API。当原始调用完成后,他会返回到控制点。
- 元数据:
- 每个blob都有自己的元数据,可以通过调用API显示的同步。
- blobstore的全局元数据,他会在每次正确执行完成关闭后自动同步。由于不正确的关闭可能会导致数据丢失,所以每次正确关闭流程很重要。
- **channels 通道:**当引用执行IO操作的时候需要使用channel,应用会对channel进行IO。 channel和线程最好是1:1数量对应关系。
IO流程
class BlobStore {
public:
typedef void *completion_t;
int open();
void close();
int put(const char *key, const char *val, uint64_t expire);
int get(const char *key, char *val, uint64_t off, size_t len);
int delete(const char *key);
int async_put(const char *key, const char *val, uint64_t expire, completion_t comp);
int async_get(const char *key, char *val, uint64_t off, size_t len, completion_t comp);
int async_delete(const char *key, completion_t comp);
};
文件读取
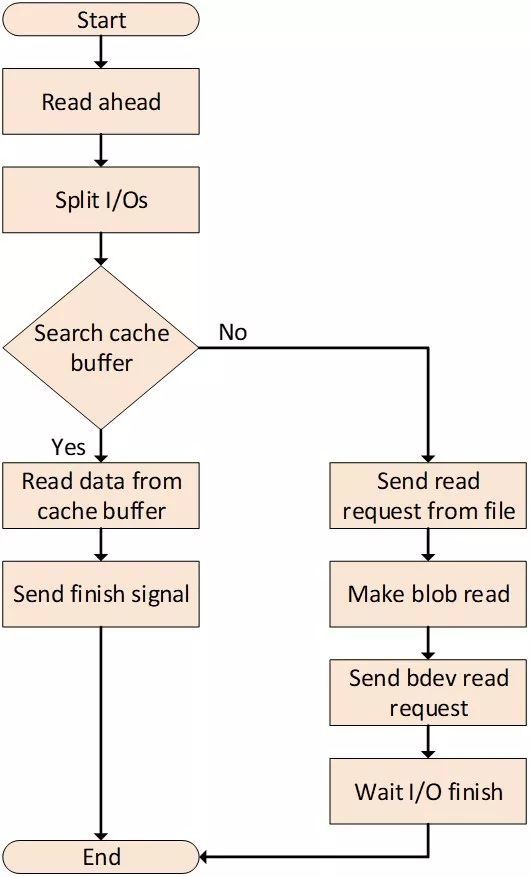
- 在文件读写时,首先会进行read ahead操作,将一部分数据从磁盘预先读取到内存的buffer中。
- 根据cache buffer的大小,对文件的I/O进行切分,使每个I/O的最大长度不超过一个cache buffer的大小。
- 对于拆分后的文件I/O,会根据其offset在cache buffer tree中查找相应的buffer。若存在,则直接从cache buffer中读取数据,进行memcpy。而对于没有缓存到cache buffer中的数据,将会对该文件的读取,转换到该文件对应的Blob进行读取。
- 对Blob读取时候,根据已打开的blob结构中记录的信息,可以获取该blob所有cluster的LBA起始位置,并根据读取位置的offset信息,计算相应的LBA地址。最后向SPDK bdev层发送异步的读请求,并等待I/O完成。BlobFS所提供的读操作为同步读,I/O完成后会在callback函数中,通过信号量通知BlobFS完成信号,至此文件读取结束。
- Cache buffer tree是由多层树结构组成。最底层Level 0叶子节点为buffer node,是用于存放数据的buffer。Level 0以上的其它层中,均为tree node,用于构建树的索引结构。
文件写入
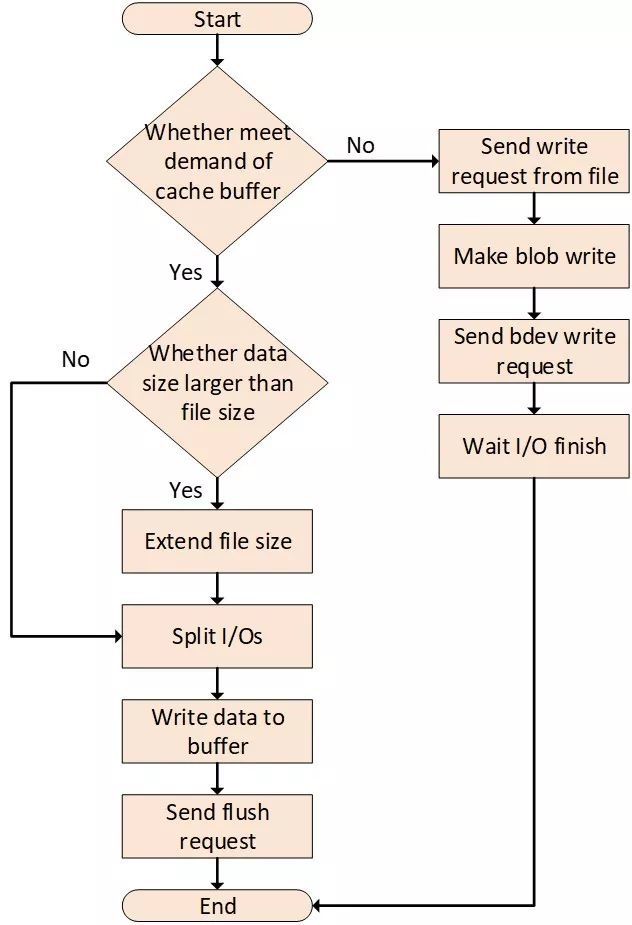
- 在进行文件写入时,首先会根据文件当前的写入位置检查是否符合cache buffer写入需求,若满足,则直接将数据写入到cache buffer中,同时触发异步的flush操作。在flush的过程中,BlobFS触发Blob的写操作,将cache buffer中的数据,写入到文件对应blob的相应位置。若不满足cache buffer的写入需求,BlobFS则直接触发文件对应的blob的写操作。
blob代码案例
/*
* We'll use this struct to gather housekeeping hello_context to pass between
* our events and callbacks.
*/
//该类为收集信息,并作为事件回调的存储信息介质
struct hello_context_t {
struct spdk_blob_store *bs;
struct spdk_blob *blob;
spdk_blob_id blobid;
struct spdk_io_channel *channel;
uint8_t *read_buff;
uint8_t *write_buff;
uint64_t io_unit_size;
int rc;
};
/*
* Free up memory that we allocated.
*/
static void
hello_cleanup(struct hello_context_t *hello_context)
{
spdk_free(hello_context->read_buff);
spdk_free(hello_context->write_buff);
free(hello_context);
}
/*
* Callback routine for the blobstore unload.
*/
static void
unload_complete(void *cb_arg, int bserrno)
{
struct hello_context_t *hello_context = cb_arg;
spdk_app_stop(hello_context->rc);
}
/*
* Unload the blobstore, cleaning up as needed.
*/
static void
unload_bs(struct hello_context_t *hello_context, char *msg, int bserrno)
{
if (hello_context->bs) {
if (hello_context->channel) {
spdk_bs_free_io_channel(hello_context->channel);
}
spdk_bs_unload(hello_context->bs, unload_complete, hello_context);
} else {
spdk_app_stop(bserrno);
}
}
/*
* Callback routine for the deletion of a blob.
*/
//13、删除blob完成
static void
delete_complete(void *arg1, int bserrno)
{
struct hello_context_t *hello_context = arg1;
SPDK_NOTICELOG("entry\n");
/* We're all done, we can unload the blobstore. */
unload_bs(hello_context, "", 0);
}
/*
* Function for deleting a blob.
*/
//12、删除blob
static void
delete_blob(void *arg1, int bserrno)
{
struct hello_context_t *hello_context = arg1;
//先关闭blob,然后再删除该blob
spdk_bs_delete_blob(hello_context->bs, hello_context->blobid,
delete_complete, hello_context);
}
/*
* Callback function for reading a blob.
*/
//11 、读blob完成后回调
static void
read_complete(void *arg1, int bserrno)
{
struct hello_context_t *hello_context = arg1;
int match_res = -1;
/* Now let's make sure things match. */
//我们测试一下看读到的数据和我们写入的数据是否相同
match_res = memcmp(hello_context->write_buff, hello_context->read_buff,
hello_context->io_unit_size);
if (match_res) {
unload_bs(hello_context, "Error in data compare", -1);
return;
} else {
SPDK_NOTICELOG("read SUCCESS and data matches!\n");
}
//关闭blob,我们写完数据了,这时也就是说我们已经将数据写入到硬盘了,那么我们可以将blob关闭了。
spdk_blob_close(hello_context->blob, delete_blob, hello_context);
}
/*
* Function for reading a blob.
*/
//10、读blob中的数据
static void
read_blob(struct hello_context_t *hello_context)
{
//还是分配一块内存给readbuffer
hello_context->read_buff = spdk_malloc(hello_context->io_unit_size,
0x1000, NULL, SPDK_ENV_LCORE_ID_ANY,
SPDK_MALLOC_DMA);
/* Issue the read and compare the results in the callback. */
//从blob中读取数据,将读到的数据放入readbuffer
spdk_blob_io_read(hello_context->blob, hello_context->channel,
hello_context->read_buff, 0, 1, read_complete,
hello_context);
}
/*
* Callback function for writing a blob.
*/
//10:写数据完成后回调
static void
write_complete(void *arg1, int bserrno)
{
struct hello_context_t *hello_context = arg1;
/* Now let's read back what we wrote and make sure it matches. */
//写完我们可以试一下读blob中的数据
read_blob(hello_context);
}
/*
* Function for writing to a blob.
*/
//9. 将数据写入blob
static void
blob_write(struct hello_context_t *hello_context)
{
SPDK_NOTICELOG("entry\n");
//要写的数据先要放到一个buffer中,所以我们需要分配一块内存给buffer
hello_context->write_buff = spdk_malloc(hello_context->io_unit_size,
0x1000, NULL, SPDK_ENV_LCORE_ID_ANY,
SPDK_MALLOC_DMA);
//使用c语言中memset函数,内存空间初始化
//memset(地址指针, 值, 大小)将地址指向的区域连续大小的内存区域填充为值
//这一步是我们将writebuffer中的数据都填充为0x5a
memset(hello_context->write_buff, 0x5a, hello_context->io_unit_size);
//在写操作钱我们需要分配IO
//在分配IO的时候我们需要将IO分配到channel上
hello_context->channel = spdk_bs_alloc_io_channel(hello_context->bs);
/* Let's perform the write, 1 io_unit at offset 0. */
//执行blob写操作,将writebuffer中的数据写入blob
spdk_blob_io_write(hello_context->blob, hello_context->channel,
hello_context->write_buff,
0, 1, write_complete, hello_context);
}
/*
* Callback function for sync'ing metadata.
*/
static void
sync_complete(void *arg1, int bserrno)
{
struct hello_context_t *hello_context = arg1;
//blob创建并且打开,并resize了,现在我们可以想blob中写入数据了
blob_write(hello_context);
}
// 7:blob大小设置完成回调函数
static void
resize_complete(void *cb_arg, int bserrno)
{
struct hello_context_t *hello_context = cb_arg;
uint64_t total = 0;
//拿到该blob的大小,看他大小是多少个cluster
total = spdk_blob_get_num_clusters(hello_context->blob);
SPDK_NOTICELOG("resized blob now has USED clusters of %" PRIu64 "\n",
total);
//手动同步blob中的元数据,当blob关闭时也会自动完成该动作。
spdk_blob_sync_md(hello_context->blob, sync_complete, hello_context);
}
// 6
/*
* Callback function for opening a blob.
*/
static void
open_complete(void *cb_arg, struct spdk_blob *blob, int bserrno)
{
struct hello_context_t *hello_context = cb_arg;
uint64_t free = 0;
hello_context->blob = blob;
//先查看blobstore中free cluster的数量,也就是实际容量抽象为多少个cluster
free = spdk_bs_free_cluster_count(hello_context->bs);
//在使用该blob之前我们需要resize一下,因为他的初始大小为0
//第一个参数为需要重置的blob,第二个参数为设置这个blob的大小,设置的单位是cluster,也就是
//需要设置这个blob有多少个cluster
//这个例子中我们将blobstore中剩余的cluster整个都放入一个blob。
spdk_blob_resize(hello_context->blob, free, resize_complete, hello_context);
}
// 5
/*
* Callback function for creating a blob.
*/
static void
blob_create_complete(void *arg1, spdk_blob_id blobid, int bserrno)
{
struct hello_context_t *hello_context = arg1;
//创建blob后系统会返回blobID
hello_context->blobid = blobid;
SPDK_NOTICELOG("new blob id %" PRIu64 "\n", hello_context->blobid);
//创建完blob后,如果要操作这个blob首先我们需要打开这个blob,打开成功后回调
spdk_bs_open_blob(hello_context->bs, hello_context->blobid,
open_complete, hello_context);
}
// 4
/*
* Function for creating a blob.
*/
static void
create_blob(struct hello_context_t *hello_context)
{
SPDK_NOTICELOG("entry\n");
//调用创建blob的接口函数,创建完成回调
spdk_bs_create_blob(hello_context->bs, blob_create_complete, hello_context);
}
// 3
/*
* Callback function for initializing the blobstore.
*/
static void
bs_init_complete(void *cb_arg, struct spdk_blob_store *bs,
int bserrno)
{
struct hello_context_t *hello_context = cb_arg;
//Get the io unit size in bytes.
//拿到io的单位大小
hello_context->io_unit_size = spdk_bs_get_io_unit_size(hello_context->bs);
//blobstore就已经初始化完成了,下面进行创建blob
create_blob(hello_context);
}
static void
base_bdev_event_cb(enum spdk_bdev_event_type type, struct spdk_bdev *bdev,
void *event_ctx)
{
SPDK_WARNLOG("Unsupported bdev event: type %d\n", type);
}
// 2。入口函数
/*
* Our initial event that kicks off everything from main().
*/
static void
hello_start(void *arg1)
{
//此时传入的参数是hello_context
struct hello_context_t *hello_context = arg1;
struct spdk_bs_dev *bs_dev = NULL;
int rc;
SPDK_NOTICELOG("entry\n");
//第一个参数指定bdev的名称,bdev可以是nvme,文件IO,或者内存
//bdev就是决定下层使用的存储介质,比如nvme或者malloc,或者文件IO
rc = spdk_bdev_create_bs_dev_ext("Malloc0", base_bdev_event_cb, NULL, &bs_dev);
//创建完bdev之后,我们需要创建blobstore,与指定的bdev设备关联上
spdk_bs_init(bs_dev, NULL, bs_init_complete, hello_context);
}
//1
int
main(int argc, char **argv)
{
struct spdk_app_opts opts = {};
int rc = 0;
struct hello_context_t *hello_context = NULL;
SPDK_NOTICELOG("entry\n");
/* Set default values in opts structure. */
//设置spdk的默认值
spdk_app_opts_init(&opts);
//设置名称
opts.name = "hello_blob";
//配置文件信息
opts.json_config_file = argv[1];
//给hello_context分配空间
hello_context = calloc(1, sizeof(struct hello_context_t));
//启动到hello_start函数中,并将hello_context作为参数传入
rc = spdk_app_start(&opts, hello_start, hello_context);
}