GANIntroduce
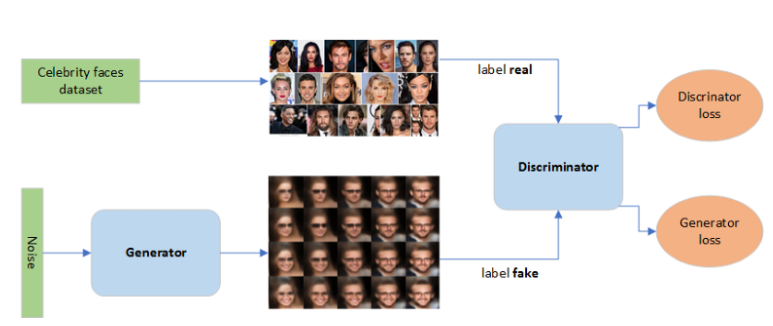
A GAN has three primary components: a generator model for generating new data, a discriminator model for classifying whether generated data are real faces, or fake, and the adversarial network that pits them against each other.
The problem of generating a new image of dog is equivalent to the problem of generating a new vector following the “dog probability distribution” over the N dimensional vector space. So we are, in fact, facing a problem of generating a random variable with respect to a specific probability distribution.
1. Converge
- Generative part : is responsible for taking N-dimensional uniform random variables (noise) as input and generating fake faces. The generator captures the probability P(X), where X is the input.
During generator training, we use the generator loss, which penalizes the generator for failing to fool the discriminator and generating a face that the discriminator classifies as fake. The discriminator is frozen during generator training and only generator’s weights are updated through backpropagation.
- Discriminative part : is a simple classifier that evaluates and distinguished the generated faces from true celebrity faces. The discriminator captures the conditional probability P(Y|X), where X is the input and Y is the label*.*
During discriminator training, we ignore the generator loss and just use the discriminator loss, which penalizes the discriminator for misclassifying real faces as fake or generated faces as real. The generator’s weights are updated through backpropagation. Generator’s weights are not updated.
2. Training Steps
-
select a number of real images from the training set;
-
generate a number of fake images, by sampling random noise vectors and creating images from them using generator;
# 随机生成均匀分布,上下边界为1和-1,输出Batch_size×100个样本 noise = np.random.uniform(-1,1,size=(Batch_size,100)) #抽取一个批量的真实照片 image_batch = X_train[index * Batch_size:(index + 1) * Batch_size] #生成的图片使用G对随机噪声进行推断 generated_images = g.predict(noise, verbose=0) -
train the discriminator for one or more epochs using both fake and real images, and update only the discriminator’s weights by labeling all the real images as 1 and the fake images as 0;

#将真实的图片和生成的图片以数组的形式拼接再一起,真实图片在上,生成图片在下 X = np.concatenate((image_batch,generated_images)) #生成真假标签,即一个包含两倍批量大小的列表,前一个批量均为1,代表真,后一个批量均为0,代表生成图片 y = [1] * Batch_size + [0] * Batch_size #判别器的损失;在一个batch的数据上进行一次参数更新 d_loss = d.train_on_batch(X,y) -
Generate another number of fake images;
#随机生成均匀分布噪声 noise = np.random.uniform(-1,1,(Batch_size,100)) -
train the full GAN model for one or more epochs using only fake images, and update only the generator’s weights by labeling all fake images as 1;

#固定D d.trainable = False #计算生成器损失;在一个batch的数据上进行一次参数更新 g_loss = d_on_g.train_on_batch(noise,[1]*Batch_size)
3. VAE(Variational Autoencoders)
by making the latent space more predictable, more continuous, less sparse. By forcing latent variables to become normally distributed, VAEs gain control over the latent space. Dataset


Learning From:

