OpenCAS介绍

Open Cache Acceleration Software (Open CAS) is an open source project encompassing
block caching software libraries, adapters, tools and more. The main goal of this cache acceleration software is toaccelerate a backend block device(s) by utilizing a higher performance device(s).
Open CAS Framework
CAS是 Intel® 通过I/O分类和在高速介质上缓存经常使用的数据来加速存储性能而开发的企业级软件解决方案。支持Linux和Windows平台。CAS通过加载到kernel的方式,将一块高速盘和慢速盘“融合”为一块盘,像其他的物理盘一样,挂载到文件系统上。因此不需要对系统或应用做任何修改就可以使用,可以认为CAS运行在内核态。
CAS 通过和内存的交互管理建立多层次的缓存,来优化系统内存的使用,同时也能够自动根据数据本身特性去确定最好的缓存分配。CAS 目前已经在业界广泛使用,能够以很小的额外成本,显著提升I/O性能。
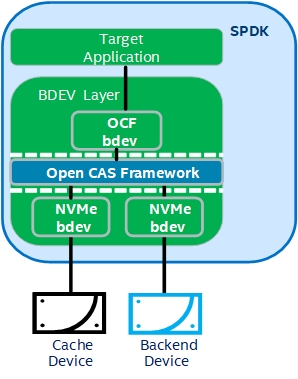
- 把大容量,慢速的存储设备称为core device, 在上图中可以认为HDD就是core device. 然后把小容量,高速的存储设备称为cache device。
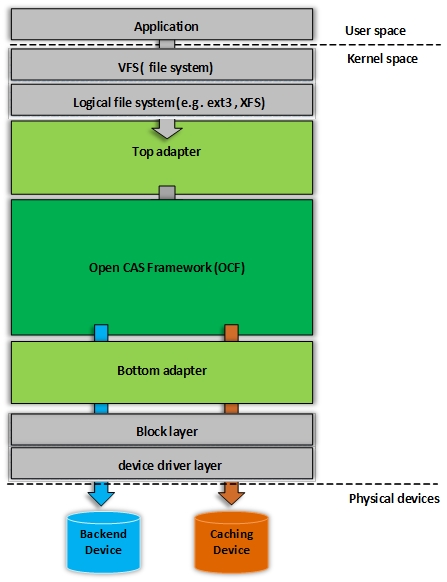
Open CAS Framwework (OCF) is
high performance block storage caching meta-library written in C. It’s entirely platform and system independent, accessing system API through user provided environment wrappers layer.
- primarily designed to
cache data from HDD drives on SSDs- caching data
from QLC SSD on TLC SSD, Optane drives, RAM memory, or any combination of above including all kinds of multilevel configurations



Cache
- a component that mediates data exchange between an application and a backend storage.
- selectively storing most accessed data on a relatively smaller and faster cache storage

cache mode
- Write-Through(WT):
I/O在写到cache device的同时,也会直接write-through到后端的core device。WT模式保证了数据在core device和cache device总是同步的,因此不用担心突然掉电造成的缓存数据丢失。因为每次数据依然要写到慢速的后端设备,所以这个模式只能够加速数据读取的过程. - Write-Back (WB):I/O写时,数据
首先写到cache device,然后就会告诉应用写完毕。这些写操作会周期性的写回到core device。这里CAS可以选择不同的cleaning policy。比如ALRU(Approximately Least Recently Used),ACP(Aggressive Cleaning Policy)或者 NOP(No Operation,即不自动写回,而由用户主动的做flush操作)。因此,WB模式能够既加速读操作,又加速写操作。但是也会有突然掉电造成缓存数据没有及时写回到core device而导致数据丢失的情况。 - Write-Around (WA):
- 缓存污染(cache pollution)。首先我们要知道cache device和core device其实是通过cache line和core line的mapping确定对应关系的。缓存污染表示
很多不常用的数据被缓存到了cache device中。那么在后面新的写I/O的情况下,没有空闲的cache line,没有足够的空间去做mapping,此时需要逐出(evict)某条对应的cache line mapping,这就造成了额外的开销。 - WA模式有点类似于WT模式,不同的是,
写操作只有在cache line有对应的core line的情况下(即这部分数据已经被读缓存过)会同时更新cache device和core device。其他情况,则直接写到core device。因此WA模式也只能加速读操作,并且保证了数据的一致性。而且还能避免缓存污染这样的情况。
- 缓存污染(cache pollution)。首先我们要知道cache device和core device其实是通过cache line和core line的mapping确定对应关系的。缓存污染表示
- Write-Invalidate(WI)
- 在这个模式中,只有
读操作会被map到缓存中。对于写操作,会直接写入到core device,同时,如果有对应的cache line在缓存中,就让这条cache line变为无效。WI模式对于读密集型I/O有更好的加速作用。并且能够减少缓存的evict操作。
- 在这个模式中,只有
- Pass-Through (PT)
很好理解,PT模式即
所有IO直接绕过cache device直接和core device交互。
core
The core object is an abstraction that allows application access to backend storage cached by a cache.
It provides
API for submitting I/O requests, which are handled according to current cache mode and other cache and core configuration parameters.During normal cache operation the backend storage is exclusively owned by the cache object, and application should never access it directly unless the core is removed from the cache. That’s it, using the core API is the only proper way of accessing the data on the backend storage.

cache line
- A cache line is the smallest portion of data that can be mapped into a cache. Every mapped cache line is associated with a core line, which is a corresponding region on a backend storage.
- cache line: core id, core line numver, valid and dirty bits

volume
- A volume is generic representation of a storage, that allows OCF to
access different types of storages using common abstract interface.- OCF uses a volume interface for accessing both backend storage and cache storage
- Storage represented by volume may be any kind of storage that allows for random block access - it may be HDD or SSD drive, ramdisk, network storage or any other kind of non-volatile or volatile memory.

Caching solutions
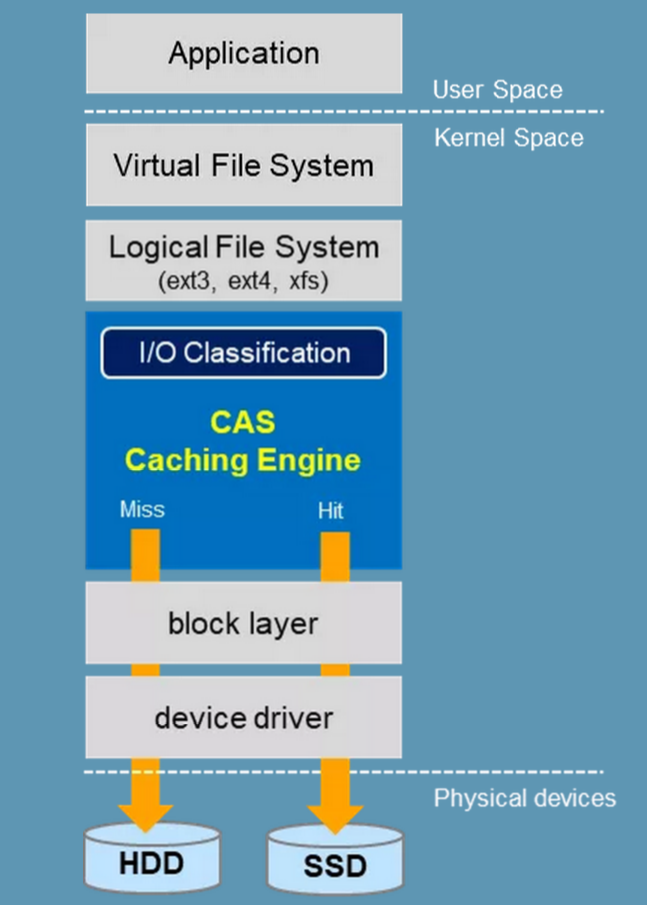
OpenCAS Linux
Open CAS Linux accelerates Linux applications by
caching active (*hot*) data to a local flash deviceinside servers.

- initial read data is retrieved from backend storage and copied to the Open CAS Linux cache. A second read promotes data to system memory. Subsequent reads are returned at high-performance RAM or flash speed.
- In Write-through mode, all data is written synchronously to both the backend storage and the cache.
- In Write-back mode, all data is written to the cache then eventually flushed to the backend storage. When the cache is full, newly identified active data evicts stale data from the cache, utilizing the Open CAS Linux proprietary eviction algorithm.
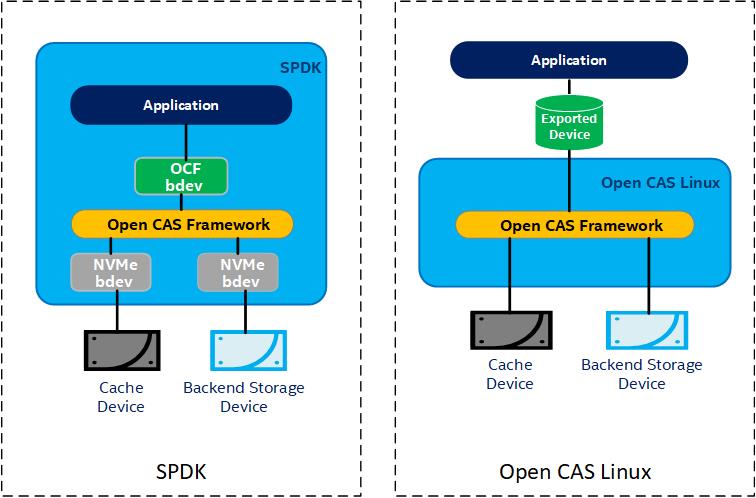
SPDK OCF Block Device