springboot缓存机制

Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术;并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化开发;
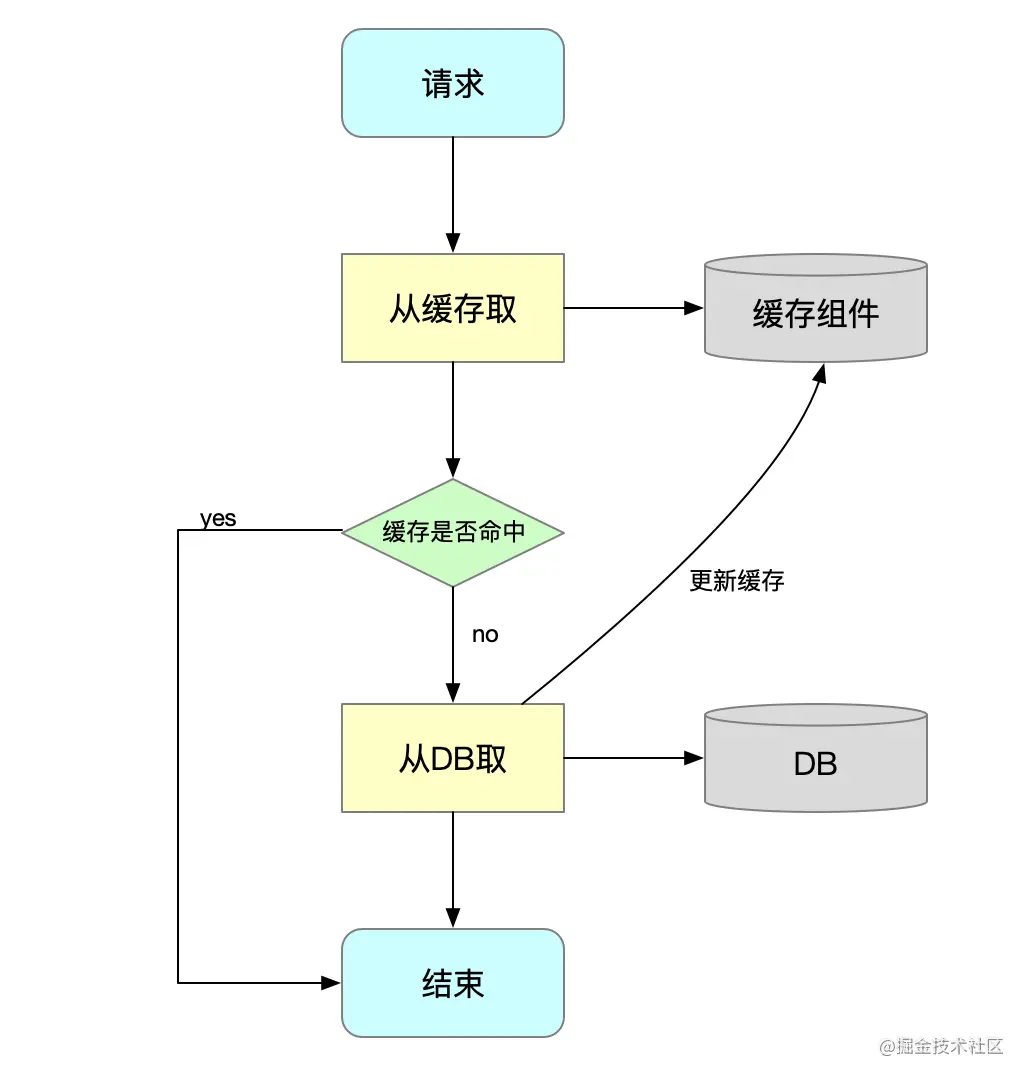
Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;Cache接口下Spring提供了各种Cache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache,ConcurrentMapCache等;- 每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,
Spring会根据参数以及目标方法检查是否已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户;下次调用直接从缓存中获取;- 使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点;
确定方法是否需要被缓存以及其缓存策略;从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据;
1. 代码解读

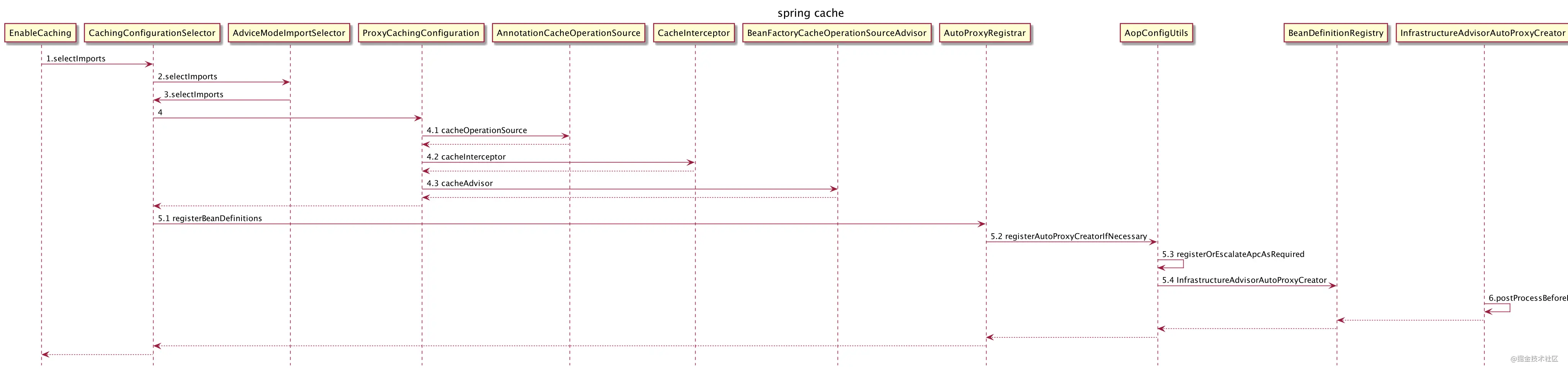
.1. 开启缓存
public class CachingConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableCaching> {
private static final String PROXY_JCACHE_CONFIGURATION_CLASS =
"org.springframework.cache.jcache.config.ProxyJCacheConfiguration";
private static final String CACHE_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME =
"org.springframework.cache.aspectj.AspectJCachingConfiguration";
private static final String JCACHE_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME =
"org.springframework.cache.aspectj.AspectJJCacheConfiguration";
private static final boolean jsr107Present;
private static final boolean jcacheImplPresent;
static {
ClassLoader classLoader = CachingConfigurationSelector.class.getClassLoader();
jsr107Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.cache.Cache", classLoader);
jcacheImplPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent(PROXY_JCACHE_CONFIGURATION_CLASS, classLoader);
}
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
return getProxyImports();
case ASPECTJ:
return getAspectJImports();
default:
return null;
}
}
private String[] getProxyImports() {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(3);
result.add(AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName());
result.add(ProxyCachingConfiguration.class.getName());
if (jsr107Present && jcacheImplPresent) {
result.add(PROXY_JCACHE_CONFIGURATION_CLASS);
}
return StringUtils.toStringArray(result);
}
private String[] getAspectJImports() {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(2);
result.add(CACHE_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME);
if (jsr107Present && jcacheImplPresent) {
result.add(JCACHE_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME);
}
return StringUtils.toStringArray(result);
}
}
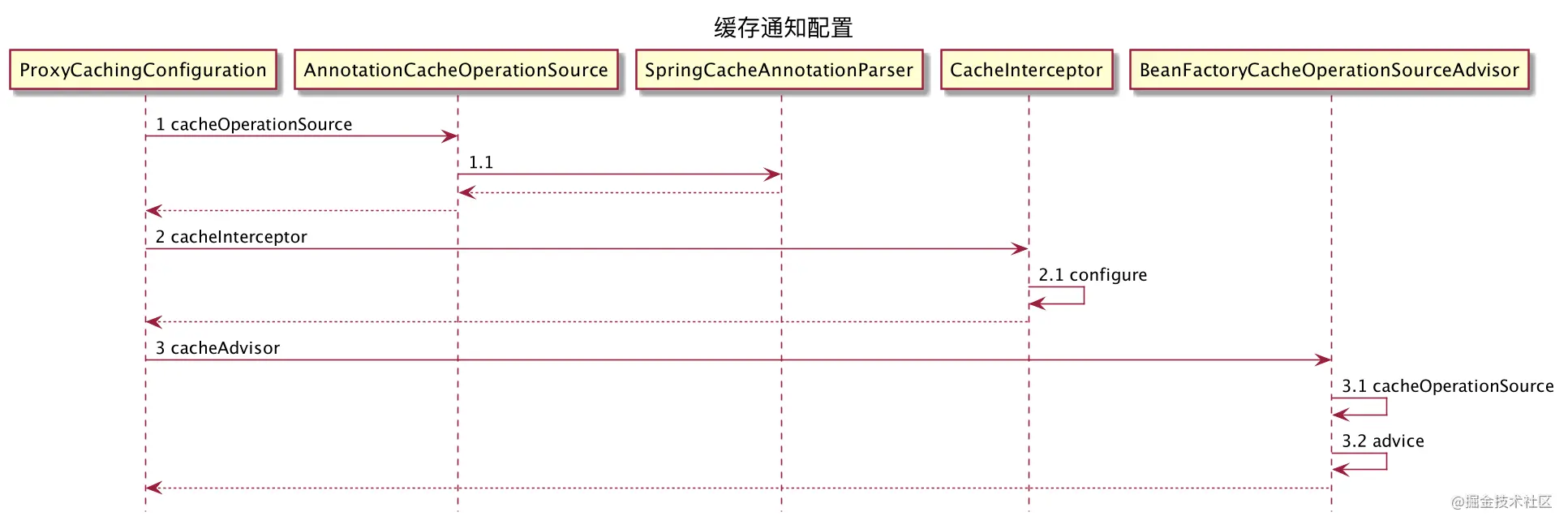
.2. 缓存通知配置
首先把
注解元数据属性解析出来,然后把用户自定义的缓存组件装配进来(CacheManager,KeyGenerator和异常处理器)
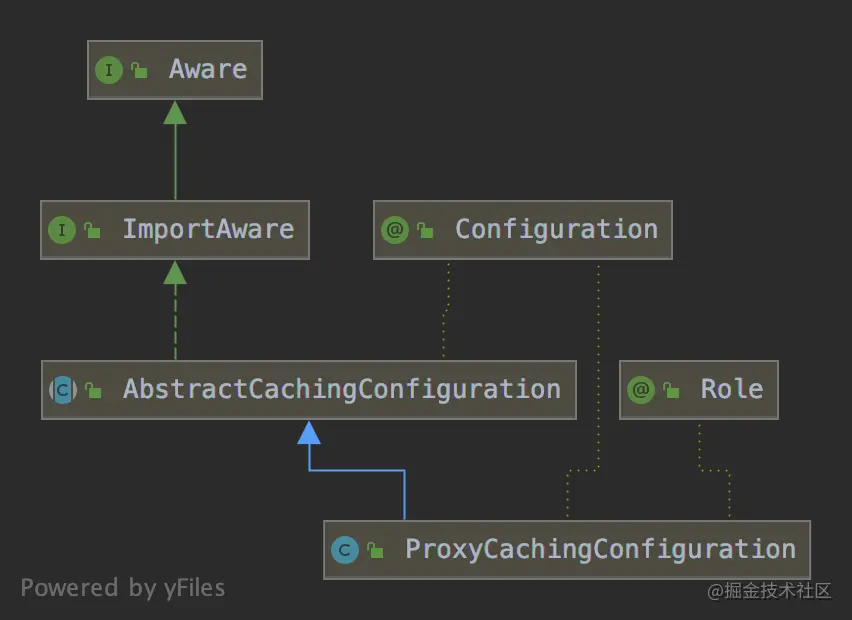
@Configuration
public abstract class AbstractCachingConfiguration implements ImportAware {
@Override
public void setImportMetadata(AnnotationMetadata importMetadata) {
this.enableCaching = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(
importMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableCaching.class.getName(), false));
if (this.enableCaching == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"@EnableCaching is not present on importing class " + importMetadata.getClassName());
}
}
@Autowired(required = false)
void setConfigurers(Collection<CachingConfigurer> configurers) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
return;
}
if (configurers.size() > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException(configurers.size() + " implementations of " +
"CachingConfigurer were found when only 1 was expected. " +
"Refactor the configuration such that CachingConfigurer is " +
"implemented only once or not at all.");
}
CachingConfigurer configurer = configurers.iterator().next();
useCachingConfigurer(configurer);
}
protected void useCachingConfigurer(CachingConfigurer config) {
this.cacheManager = config::cacheManager;
this.cacheResolver = config::cacheResolver;
this.keyGenerator = config::keyGenerator;
this.errorHandler = config::errorHandler;
}
}
@Configuration
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class ProxyCachingConfiguration extends AbstractCachingConfiguration {
@Bean(name = CacheManagementConfigUtils.CACHE_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor cacheAdvisor() {
BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setCacheOperationSource(cacheOperationSource());
advisor.setAdvice(cacheInterceptor());
if (this.enableCaching != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableCaching.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public CacheOperationSource cacheOperationSource() {
return new AnnotationCacheOperationSource();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public CacheInterceptor cacheInterceptor() {
CacheInterceptor interceptor = new CacheInterceptor();
interceptor.configure(this.errorHandler, this.keyGenerator, this.cacheResolver, this.cacheManager);
interceptor.setCacheOperationSource(cacheOperationSource());
return interceptor;
}
}
.3. 缓存代理设置
.4. 缓存设置
final class CacheConfigurations {
private static final Map<CacheType, Class<?>> MAPPINGS;
static {
Map<CacheType, Class<?>> mappings = new EnumMap<>(CacheType.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.GENERIC, GenericCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.EHCACHE, EhCacheCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.HAZELCAST, HazelcastCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.INFINISPAN, InfinispanCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.JCACHE, JCacheCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.COUCHBASE, CouchbaseCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.REDIS, RedisCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.CAFFEINE, CaffeineCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.SIMPLE, SimpleCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.NONE, NoOpCacheConfiguration.class);
MAPPINGS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(mappings);
}
public static String getConfigurationClass(CacheType cacheType) {
Class<?> configurationClass = MAPPINGS.get(cacheType);
Assert.state(configurationClass != null, () -> "Unknown cache type " + cacheType);
return configurationClass.getName();
}
public static CacheType getType(String configurationClassName) {
for (Map.Entry<CacheType, Class<?>> entry : MAPPINGS.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue().getName().equals(configurationClassName)) {
return entry.getKey();
}
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unknown configuration class " + configurationClassName);
}
}
- CacheAutoConfiguration
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(CacheManager.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(CacheAspectSupport.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = CacheManager.class, name = "cacheResolver")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ CouchbaseAutoConfiguration.class, HazelcastAutoConfiguration.class,
HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class, RedisAutoConfiguration.class })
@Import(CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public class CacheAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public CacheManagerCustomizers cacheManagerCustomizers(
ObjectProvider<CacheManagerCustomizer<?>> customizers) {
return new CacheManagerCustomizers(
customizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
@Bean
public CacheManagerValidator cacheAutoConfigurationValidator(
CacheProperties cacheProperties, ObjectProvider<CacheManager> cacheManager) {
return new CacheManagerValidator(cacheProperties, cacheManager);
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(AbstractEntityManagerFactoryBean.class)
protected static class CacheManagerJpaDependencyConfiguration
extends EntityManagerFactoryDependsOnPostProcessor {
public CacheManagerJpaDependencyConfiguration() {
super("cacheManager");
}
}
}
.1. rediscache
RedisCacheConfiguration注入了RedisCacheManager类型的bean,该配置生效有几个条件:
- 只有应用引入了redis依赖并且定义了RedisConnectionFactory
- 没有定义其他类型的CacheManager
- spring.cache.type属性为redis
- 在RedisAutoConfiguration之后配置
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(RedisConnectionFactory.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(RedisAutoConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(RedisConnectionFactory.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CacheManager.class)
@Conditional(CacheCondition.class)
class RedisCacheConfiguration {
private final CacheProperties cacheProperties;
private final CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker;
private final org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration;
RedisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties,
CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker,
ObjectProvider<org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration> redisCacheConfiguration) {
this.cacheProperties = cacheProperties;
this.customizerInvoker = customizerInvoker;
this.redisCacheConfiguration = redisCacheConfiguration.getIfAvailable();
}
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory,
ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
RedisCacheManagerBuilder builder = RedisCacheManager
.builder(redisConnectionFactory)
.cacheDefaults(determineConfiguration(resourceLoader.getClassLoader()));
List<String> cacheNames = this.cacheProperties.getCacheNames();
if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {
builder.initialCacheNames(new LinkedHashSet<>(cacheNames));
}
return this.customizerInvoker.customize(builder.build());
}
private org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration determineConfiguration(
ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (this.redisCacheConfiguration != null) {
return this.redisCacheConfiguration;
}
Redis redisProperties = this.cacheProperties.getRedis();
org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration config = org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
.defaultCacheConfig();
config = config.serializeValuesWith(SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer(classLoader)));
if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {
config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());
}
if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {
config = config.prefixKeysWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());
}
if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {
config = config.disableCachingNullValues();
}
if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {
config = config.disableKeyPrefix();
}
return config;
}
}
- redisAutoConfiguration
RedisAutoConfiguration依赖redis,并且导入了LettuceConnectionConfiguration和JedisConnectionConfiguration连接配置(此处不展开分析),定义了RedisTemplate和StringRedisTemplate两个bean供RedisCacheManager使用。
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(RedisOperations.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisProperties.class)
@Import({ LettuceConnectionConfiguration.class, JedisConnectionConfiguration.class })
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException {
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
}
.5. 默认设置
static class CacheConfigurationImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
CacheType[] types = CacheType.values();
String[] imports = new String[types.length];
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
imports[i] = CacheConfigurations.getConfigurationClass(types[i]);
}
return imports;
}
}
public enum CacheType {
/**
* Generic caching using 'Cache' beans from the context.
*/
GENERIC,
/**
* JCache (JSR-107) backed caching.
*/
JCACHE,
/**
* EhCache backed caching.
*/
EHCACHE,
/**
* Hazelcast backed caching.
*/
HAZELCAST,
/**
* Infinispan backed caching.
*/
INFINISPAN,
/**
* Couchbase backed caching.
*/
COUCHBASE,
/**
* Redis backed caching.
*/
REDIS,
/**
* Caffeine backed caching.
*/
CAFFEINE,
/**
* Simple in-memory caching.
*/
SIMPLE,
/**
* No caching.
*/
NONE
}
2. 使用方式
- 引入缓存依赖相关包文件
- 在应用启动类添加@EnableCaching注解
- 在业务方法添加@Cacheable注解,进行使用
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
.1. 重要概念
| 名称 | 解释 |
|---|---|
Cache |
缓存接口,定义缓存操作;实现有RedisCache、EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache等 |
CacheManager |
缓存管理器,管理各种缓存(cache)组件 |
| 名称 | 解释 |
|---|---|
@Cacheable |
主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其进行缓存 |
@CacheEvict |
清空缓存 |
@CachePut |
保证方法被调用,又希望结果被缓存;与@Cacheable区别在于,@CachePut会缓存结果,并且会执行方法,常用于更新 |
@EnableCaching |
开启基于注解的缓存,用于添加在springboot启动类上 |
@CacheConfig |
统一配置本类的缓存注解的属性,用于类上 |
| 名称 | 解释 |
|---|---|
value |
缓存的名称,即cacheNames属性,必须指定至少一个;例如,@Cacheable(value=”mycache”)或者@Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
key |
缓存的key,可以为空,如果指定,必须要按照SpEL表达式编写, 如果不指定,则默认按照方法的所有参数进行组合;例如,@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#id”) |
condition |
缓存的条件,可以为空,使用SpEL编写,返回true或者false, 只有为true才进行缓存/清除缓存;例如,@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
unless |
否定缓存;当条件结果为true时,就不会缓存;@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,unless=”#userName.length()>2”) |
allEntries |
@CacheEvict中属性,是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为false,如果指定为true, 则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存;例如,@CachEvict(value=”testcache”, allEntries=true) |
beforeInvocation |
@CacheEvict中属性,是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为false,如果指定为 true, 则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存,缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存;例如,@CachEvict(value=”testcache”,beforeInvocation=true) |
.2. SpEL 上下文数据
| 名称 | 位置 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
methodName |
root对象 |
当前被调用的方法名 | #root.methodname |
method |
root对象 |
当前被调用的方法 | #root.method.name |
target |
root对象 |
当前被调用的目标对象实例 | #root.target |
targetClass |
root对象 |
当前被调用的目标对象的类 | #root.targetClass |
args |
root对象 |
当前被调用的方法的参数列表 | #root.args[0] |
caches |
root对象 |
当前方法调用使用的缓存列表 | #root.caches[0].name |
Argument Name |
执行上下文 | 当前被调用的方法的参数,如findArtisan(Artisan artisan),可以通过#artsian.id获得参数 |
#artsian.id |
result |
执行上下文 | 方法执行后的返回值(仅当方法执行后的判断有效,如unless cacheEvict的beforeInvocation=false) |
#result |
- 当要使用
root对象的属性作为key时,也可以将#root省略,因为Spring默认使用的就是root对象的属性;
@Cacheable(key = "targetClass + methodName +#p0")Copy
- 使用方法参数时,可以直接使用
#参数名或者#p参数index
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#id")
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#p0")
| 类型 | 运算符 |
|---|---|
| 关系 | < , > , <= , >= , == , != , lt , gt , le , ge , eq , ne |
| 算术 | + , - , * , / , % , ^ |
| 逻辑 | `&& , |
| 条件 | ?:(ternary) , ?:(elvis) |
| 正则表达式 | matches |
| 其他类型 | ?. , ?[…] , ![…] , ^[…] , $[…] |
.3. 缓存实战
<!-- spring cache -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
@SpringBootApplication
// 开启缓存
@EnableCaching
public class SpringbootLab2CacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootLab2CacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Cacheable注解会先查询是否已经有缓存,有则使用缓存,不执行方法,没有则会执行方法并缓存;
此处的
value是必需的,它指定了缓存存放的命名空间;此处的
key是使用的spEL表达式;这里有一个小坑,如果把methodName换成method运行会报错,观察它们的返回类型,原因在于methodName是String而methoh是Method;此处的
User实体类一定要实现序列化public class User implements Serializable,否则会报java.io.NotSerializableException异常;
@Cacheable(value = "user_query_1" ,key = "#name + '--' + #mobile", unless = "#result == null")
public User getUser(String name, String mobile){
log.info("Service层getUser方法执行了");
return testDao.getUser(name, mobile);
}
String[] cacheNames() default {}; // 命名空间,和value注解一样,与value二选一使用
String keyGenerator() default ""; // key的生成器,key/keyGenerator二选一使用
String cacheManager() default ""; // 指定缓存管理器
String cacheResolver() default ""; // 指定获取解析器
String condition() default ""; // 条件符合则缓存
String unless() default ""; // 条件符合则不缓存
boolean sync() default false; // 是否使用异步模式Copy
当类中需要缓存的方法很多,可以在类上添加
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = {"myCache"})注解来统一指定value的值,这时方法上的注解可省略value,如果在方法依旧写上了value,那么依然以方法的value值为准(就近原则);
@Log4j2
@Service
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "user_query_2")
public class Test1Service {
@Resource
private TestDao testDao;
@Cacheable(key = "#name + '--' + #mobile", unless = "#result == null")
public User getUser1(String name, String mobile){
log.info("Service层getUser1方法执行了");
return testDao.getUser(name, mobile);
}
@Cacheable(value = "user_query_3", key = "#name", unless = "#result == null")
public User getUser2(String name, String mobile){
log.info("Service层getUser2方法执行了");
return testDao.getUser(name, mobile);
}
}
String keyGenerator() default ""; // key的生成器,key/keyGenerator二选一使用
String cacheManager() default ""; // 指定缓存管理器
String cacheResolver() default ""; // 指定获取解析器
@CachePut注解的作用主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,和@Cacheable不同的是,它每次都会触发真实方法的调用;简单来说就是用户更新缓存数据,但需要注意的是该注解的value和key必须与@Cacheable更新的缓存相同,否则会新增根据key,新增一条缓存;或者业务需要在读取缓存的同时也必须执行方法,也可使用此注解;
@CachePut(value = "user_query_4", key = "#name + '--' + #mobile", unless = "#result == null")
public User update(String name, String mobile){
log.info("Service层update方法执行了");
return testDao.getUser(name, mobile);
}
String[] cacheNames() default {}; // 命名空间,和value注解一样,与value二选一使用
String keyGenerator() default ""; // key的生成器,key/keyGenerator二选一使用
String cacheManager() default ""; // 指定缓存管理器
String cacheResolver() default ""; // 指定获取解析器
String condition() default ""; // 条件符合则缓存
String unless() default ""; // 条件符合则不缓存
@CachEvict的作用主要针对方法配置,能够根据一定的条件对缓存进行清空;
| 属性 | 解释 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
allEntries |
是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为false,如果指定为true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存 |
@CachEvict(value=”testcache”,allEntries=true) |
beforeInvocation |
是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为false,如果指定为true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存,缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存 |
@CachEvict(value=”testcache”,beforeInvocation=true) |
// 清除一条缓存,key为要清空的数据
@CacheEvict(value="user_query_4", key="#name + '--' + #mobile")
public void delete(String name, String mobile){
log.info("Service层delete方法执行了, key = {}", name + "--" + mobile);
}
// 方法调用后, 清空所有缓存
@CacheEvict(value="user_query_4", allEntries=true)
public void deleteAll() {
log.info("Service层deleteAll方法执行了, cacheNames = user_query_4");
}
// 方法调用前, 清空所有缓存
@CacheEvict(value="user_query_4", beforeInvocation=true)
public void deleteAllBefore() {
log.info("Service层deleteAllBefore方法执行了, cacheNames = user_query_4");
}
String[] cacheNames() default {}; // 命名空间,和value注解一样,与value二选一使用
String keyGenerator() default ""; // key的生成器,key/keyGenerator二选一使用
String cacheManager() default ""; // 指定缓存管理器
String cacheResolver() default ""; // 指定获取解析器
String condition() default ""; // 条件符合则清空Copy
.4. 整合 Redis
.1. properries 配置文件
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=0
# Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=123456
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.pool.max-active=1000
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.max-idle=10
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.min-idle=2
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
spring.redis.timeout=0
.2. RedisTemplate 配置
@Configuration
public class RedisConfiguration {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
// 使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer来序列化和反序列化redis的value值(默认使用JDK的序列化方式)
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
// 设置值value的序列化方式
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(serializer);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(serializer);
// 设置键key的序列化方式
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}
.3. 解决 Redis 缓存乱码问题
@Configuration
public class SpringCacheRedisConfig {
private Duration timeToLive = Duration.ofSeconds(60);
public void setTimeToLive(Duration timeToLive) {
this.timeToLive = timeToLive;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
//解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 配置序列化(解决乱码的问题)
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(timeToLive)
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer))
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}
}Copy
.5. 基于 Caffeine 的 CacheManager
Spring Cache支持自定义缓存管理器CacheManager,这里就推荐一个比较好用的CacheManager,基于Caffeine算法的CacheManager;
<!-- 用于创建基于Caffeine的CacheManager -->
<!-- 如果采用默认的CacheManager可以不加下面依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>30.1.1-jre</version>
</dependency>Copy
.1. 注册缓存管理器
public class CacheConfiguration {
/**
* 创建基于Caffeine的CacheManager
*/
@Bean
@Primary // 保证Spring优先使用
public CacheManager caffeineCacheManager() {
SimpleCacheManager cacheManager = new SimpleCacheManager();
List<CaffeineCache> caches = new ArrayList<>(Caches.values().length);
for (Caches c : Caches.values()) {
caches.add(new CaffeineCache(c.name(),
Caffeine.newBuilder().recordStats()
.expireAfterWrite(c.getTtl(), TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.maximumSize(c.getMaxSize())
.build())
);
}
cacheManager.setCaches(caches);
return cacheManager;
}
@Bean
public LoadingCache<String, Object> loadingCache() {
return CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(3000).expireAfterWrite(3600, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build(new CacheLoader<String, Object>() {
@Override
public Object load(String name) {
return null;
}
});
}
}Copy
.2. 配置缓存池
@Getter
public enum Caches {
/**
* 配置的缓存nameCaches
* 将系统中设置的nameCaches作为enum添加进来
* 可以配置nameCaches中不同key的最大容量,以及缓存的过期时间
*/
user_query_1(3600, 20),
user_query_2(3600, 20),
user_query_3(3600, 20),
user_query_4(3600, 20),
;
public static final int DEFAULT_TTL = 10;
public static final int DEFAULT_MAXSIZE = 5000;
Caches() {
}
Caches(int ttl) {
this.ttl = ttl;
}
Caches(int ttl, int maxSize) {
this.ttl = ttl;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
private int maxSize = DEFAULT_MAXSIZE; // 最大數量
private int ttl = DEFAULT_TTL; // 过期时间(秒)
}Copy