Wavelet

- Fourier Transform is the dot product between real signal and various frequency of sine wave. We get a stats of frequency but we don’t know when that “frequency” happen, we lost the time resolution of the real signal.
- To get both frequency and time resolution we can be
dividing the original signal into several partsand apply Fourier Transform to each part. The problem of STFT is the choice of time windows; low frequencies require large time windows and high frequencies need a short time windows to provide required resolution in time and frequency.- Wavelets come as a solution to the lack of Fourier Transform. we need a bigger time window to catch low frequency and smaller window for higher frequency and That is the Idea of Wavelets.
- simultaneous localization both in frequency spectrogram& time;
- Sparsity of the representation: Many of the coefficients c(j,k) in a wavelet representation are either zero or very small
- linear computational time complexity
1. Formula
Where x is the real signal, ψ is an arbitrary mother wavelet, a is the scale and b is the translation (X is the processed signal of course). The scale is the same as the size of the window.
- Non zero magnitudes of the mother wavelet are “the window”
- wavelet has many kinds of mother wavelet and you can define a new one (with several requirements that need to satisfy of course)
- Fourier Transform just has 1 kind of transformation but Wavelet Transform can have many kinds of transformation
- The scale is inversely proportional to the frequency of the mother wavelet (the window).
- The approximation, or scaling, coefficients are the
lowpass representation of the signalandthe details are the wavelet coefficients.At each subsequent level,the approximation coefficientsare divided into a coarserapproximation (lowpass) and highpass (detail) part.



2. Wavelet Transform
- Mother wavelet: a wavelet function
- characterizes the basic wavelet shape
- be oscillatory and have a finite energy
- Father wavelet: a scaling function
- characterizes the basic wavelet scale
- allow to express needed details of the approximated function in the domain of interest;
- Daughter wavelets: all other derived wavelets
- generating function( scale & shifts)
.1. Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT)
CWT is a Wavelet Transform where we can set the scale and translation arbitrary.
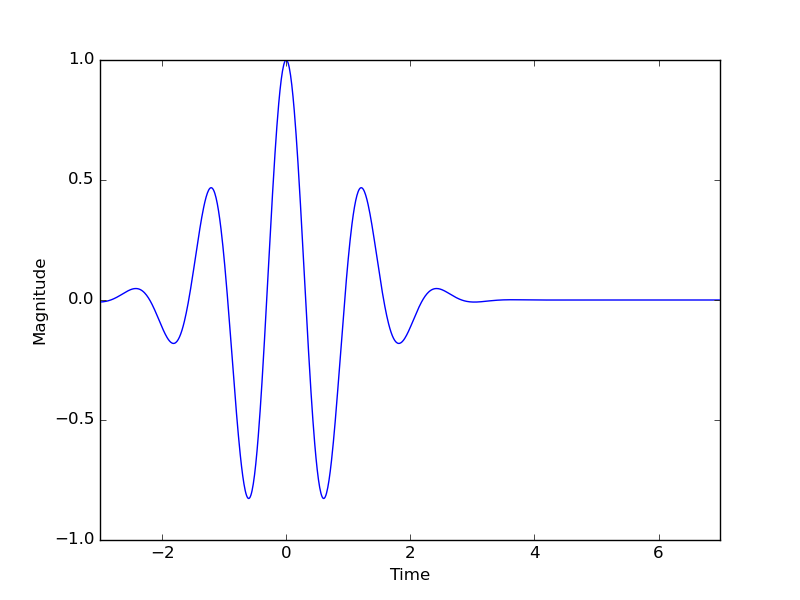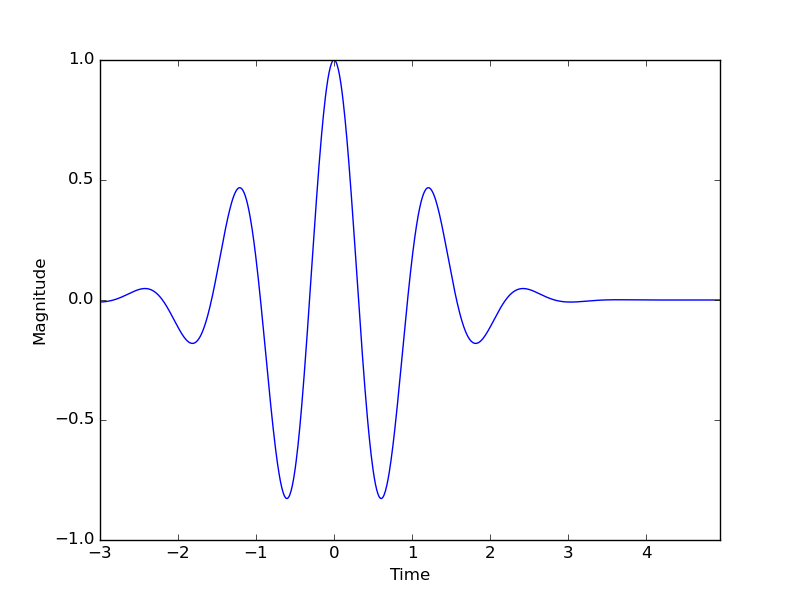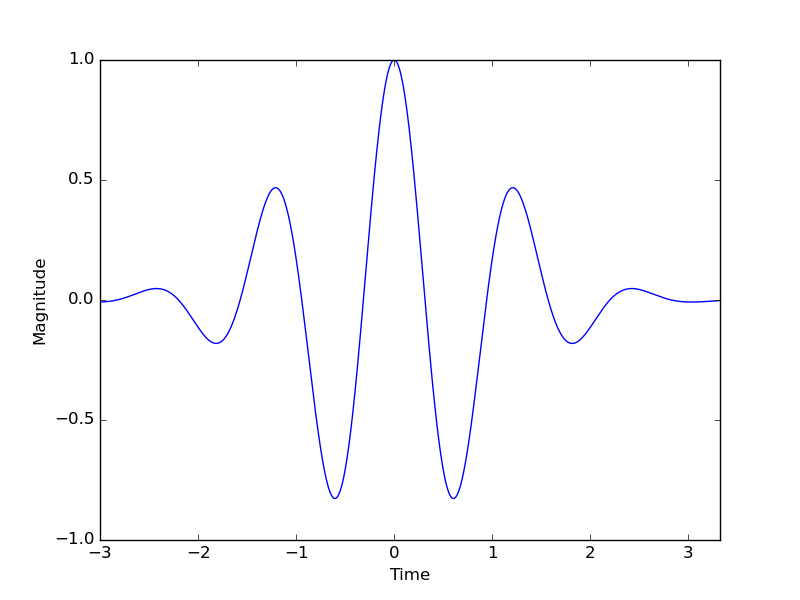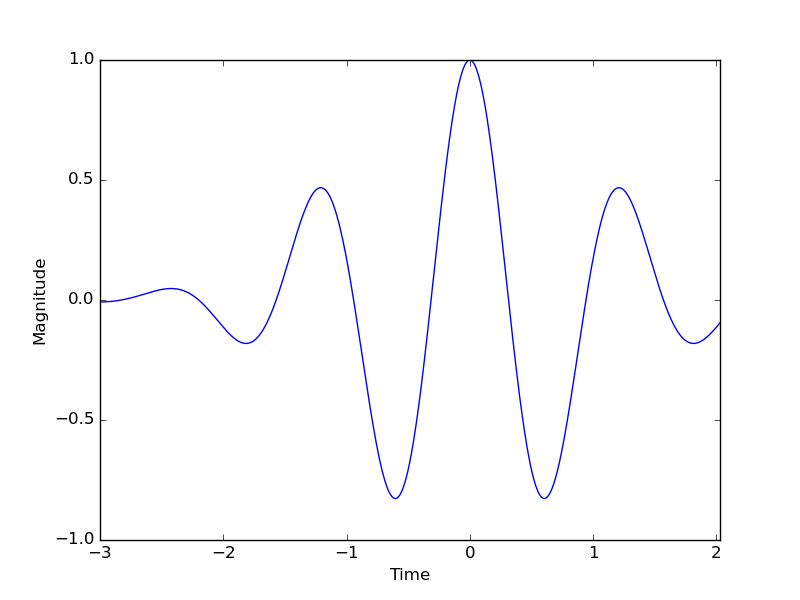
- Morlet Wavelet

- Meyer Wavelet

- Mexican Hat Wavelet

.2. Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT)
DWT is a kind of wavelets that restrict the value of scale and translation. The restriction is like the scale is increasing in the power of 2 (a = 1, 2, 4, 8,…) and the translation is the integer (b = 1, 2, 3, 4, …).

- Haar Wavelet

- Daubechies Wavelet

.1. .1. Wavelet Denoising(Fast Wavelet Transform)
-
perform a multilevel wavelet decomposition




-
Identify a thresholding technique
- the universal threshold
- SureShrink or the rigrsure method
- the Heursure method
- the minimax method
-
threshold and reconstruction
- soft and hard thresholding

.2. 2D discrete wavelet transform



3. Application
.1. communication
handle non stationary behaviorandto segregate information into uncorrelated segments. This section provides a brief about various methodologies to extract benefits of wavelets into communication systems.
Wavelet based OFDM systemsprovides improved Bit Error Rate (BER) and peak-to-average-power ratio (PAPR) performance compared to conventional OFDM system using FFT. Due to large number of sub band carriers, OFDM has high PAPR and makes it sensitive to nonlinear effects. Wavelet based system controls the PAPR ratio and results in improved performance compared to FFT based systems.
.2. data/image Detection
- represent functions with discontinuities or corners (images)
- some wavelets have discontinuities themselves or sharp corners in 2D cases.
Bio medical signals are generally
one dimensional time series data (Electro Cardiogram- ECG, electroencephalogram -EEG)oran image (X ray, ultrasound scan, MRI). Accordingly a1D or 2D wavelet transformcan be used to process the signal. Wavelet transform helps todivide the signal to uncorrelated sub bands due to orthogonality property.The transform coefficients or a part of it (say certain level coefficients) are used as feature for classifying the signal is a common methodology that can be adopted for a variety of applications. Recent advancement inneural networks like CNN with wavelet coefficients as input featuresopens up stage for a wide variety of research solutions. Another promising category of application is in signal preprocessing toremove unwanted information in biomedical signals[9]with thresholding techniques.
.1. EEG signal processing
selection of wavelets, level of transform, threshold calculations, selection of neural network of appropriate level and availability of data to train the network to achieve a desired accuracy.

.2. cancer detection
wavelet decomposition coefficients are used to extract features by calculating 2 level Haar wavelet transform and extract mean, standard deviation and energy of the transform coefficients as features for extraction of abnormal areas in image.
.4. compression
JPEG image compression technique is the standard technique used. It uses Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) for the frequency domain conversion followed by Huffman coding.



